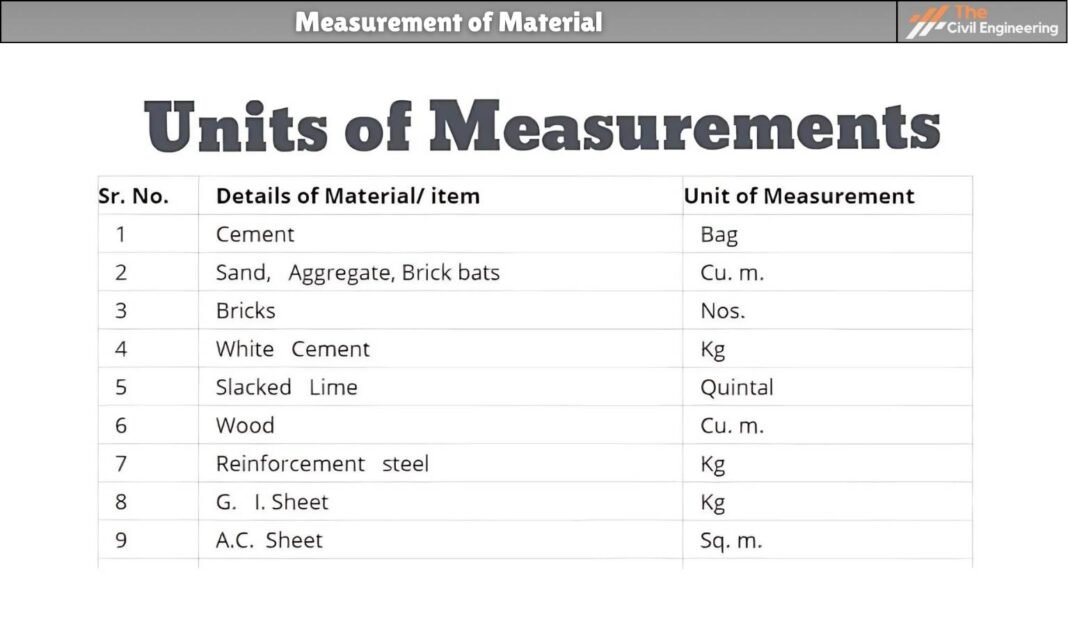
In this article, we will discuss measurement of materials.
1. Introduction
The materials used in construction are measure differently for different materials. The bricks, blocks are measured in number while cement is measured in weight.
2. Measurement of Materials
The materials used for preparation of concrete are
(i) cement
(ii) fine aggregate
(iii) coarse aggregate and
(iv) water
Their accurate measurement before mixing is very important so that the required quantities in the proportion of the concrete mix are obtained. Here is measurement of material used in concrete.
2.1. Cement
It is preferable to measure cement in terms of its weight, and not in terms of volume. The volume of cement changes with the conditions of measurement. In our country, cement is supplied in bags, each bag weighing 50 kg. Under normal conditions, the volume of cement in the bag is considered equivalent to 34.5 liters. However, if the same cement is shovelled, the bag may measure up to 42 liters. Before mixing, therefore, cement is measured in terms of weight.
2.2. Fine aggregates
Fine aggregate (i.e. sand), may be measured by weight, for accurate works and by volume for ordinary works. However, when dry sand absorbs water from atmosphere, or when water is mixed to it artificially, its volume increases. This increases in volume due to moisture in sand is known as ‘bulking of sand’. Water particles lubricate the sand particles, causing surface tension, and due to this particles are pulled apart. Thus increase in volume results. This increase in volume depends on the gradation of sand, but may be taken to be maximum at a moisture content of about 4% by weight of dry sand. Further increase in moisture results in decrease in the percent increase of volume.
The bilking increases with fineness, and may be about 25% by volume Due to this, if sand is measured by volume, bulking should be properly accounted for Knowing the percentage bulking at the site, actual volume of corresponding dry sand can be estimated by subtracting from the measured volume of sand the increase in volume due to bulking. For accurate and large scale works, sand is always measure( by weight and necessary allowance is made for the hygroscopic moisture in the sand.
| Read Also: ABC Classification of Construction Materials |
3.3. Coarse aggregate
There is no problem of bulking in coarse aggregate, an hence it may be measured either by volume or by weight. However, the weight a a given volume of aggregate is influenced by the size of the measuring box. Hence, the accurate and large scale works, measurement should be done by weight. The unit weight of coarse aggregate in loose and dry state is found exactly in the same manner as for fine aggregate, except that a bigger container is used. Since the size of contai.ne has effect on the determinations, Indian Standard specify the following sizes of contain! for carrying out the tests :
1. Maximum size of aggregate 5 mm to 40 mm 15 liter capacity cylinder of 25 cm diameter.
2. Maximum size of aggregate over 40 mm : 40 liter capacity cylinder of 35 cm diameter.
3.4. Water
Water is normally measured by volume, and specified as so many liters per bag of cement. For a given quantity of water to be mixed in concrete, adjustments should be made for the amount of water present in sand and aggregate. The amount for the water present in the aggregate, due to hygroscopic action etc., should be substracted from the total required quantity of water.
However, if the aggregate is dry, and found to absorb water, extra water should be added to account for this. The percentage absorption should be determined first.
Read More: Types of Vibrators in Construction
Read More: Segregation in Concrete