| In this article, we will discuss the eight purposes of dams briefly. |
The dam is an essential civil engineering structure that has paramount importance in various fields of engineering such as irrigation engineering, hydropower engineering, navigation, and so on.
A dam may be defined as a structure constructed to obstruct the flow of water or underground flowing water and streams, thereby forming reservoirs that can be useful for supplying water for irrigation, industrial use, electricity generation, navigation, human use, etc.
The dam can also serve as a protective structure for suppressing the flood.
One of the primary purposes of the dam is the diversion of water, retention of water, and control of water.
Ever since the dawn of civilization in Mesopotamia, the man began to develop the concept of dams, particularly for controlling river water levels.

The earliest dam ever constructed dates back to 3000 BC and is located in Jordan. It is known as the Jawa Dam.
Some of the dams serve as engineering structures and tourist attraction centers.
Such fascinating dams include Gordon Dam, Contra Dam, Monticello Dam, etc.
1. Purposes of Dam
In today’s construction world, any work involving water resources inevitably consists of constructing a dam to raise the water level or storing water.
According to the recent reports of the World Register of Dams, about 48% of the dams are constructed for irrigation, 17% of the dams for the generation of electricity (hydropower), 13% of the dams for water supply, 10% of them for flood control, 5% of the dams for recreational purpose and about 1% of the dams are used for navigational works and fish farming.
The various purposes of the dam can be summarized as follows:
i. Irrigation
As discussed earlier, irrigation tops the list of the various purposes served by dams. Currently, irrigated land covers approximately 18% of the world’s arable land, and providing water for such massive land areas is hectic and problematic.
Due to the limited availability of water resources, the dam is usually constructed to retain water that can be duly utilized for irrigation.
Moreover, the total irrigated land produces only 40% of crop output, which is insufficient for the growing population.
Hence, dams play a vital role in storing and providing water for irrigation worldwide.
According to the World Commission on Dam reports, approximately 30 to 40% of the irrigated land depends upon dams for water supply.
Also, about 60% of the crop produced is dependent on the water provided by the dam for their irrigation.
If dams are constructed and irrigation fostered, it will benefit the rural population and help uplift their socio-economic condition. Thus, a dam can be regarded as the lifeline of irrigation.
For example: The Burrinjuck Dam is an irrigation dam located in Australia which was constructed as the main headwater storage for Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area in New South Wales.

Figure: Burrinjuk Dam, an irrigation dam in Australia
ii. Hydropower
The generation of electricity by utilizing water resources, i.e., hydroelectric power generation, constitutes about 24% of the world’s electricity.
The combined capacity of hydropower plants worldwide is roughly equal to 675000 Megawatts producing 2.3 trillion kilowatts of electricity annually.
Dams are an essential component of such hydropower plants and are inevitable for hydroelectricity generation.
Hydroelectricity constitutes about 90% of the world’s renewable energy, which is produced utilizing the functions that a dam serves, i.e., water retention.
Some of the examples of dams that have been constructed for hydro-electricity generation are listed as follows:
1. Three Gorges Dam, China (installed capacity of 22500 MW)
2. Itaipu Dam, Brazil ( installed capacity of 14,000 MW)
3. Belo Monte Dam, Brazil ( installed capacity of 11,233 MW)
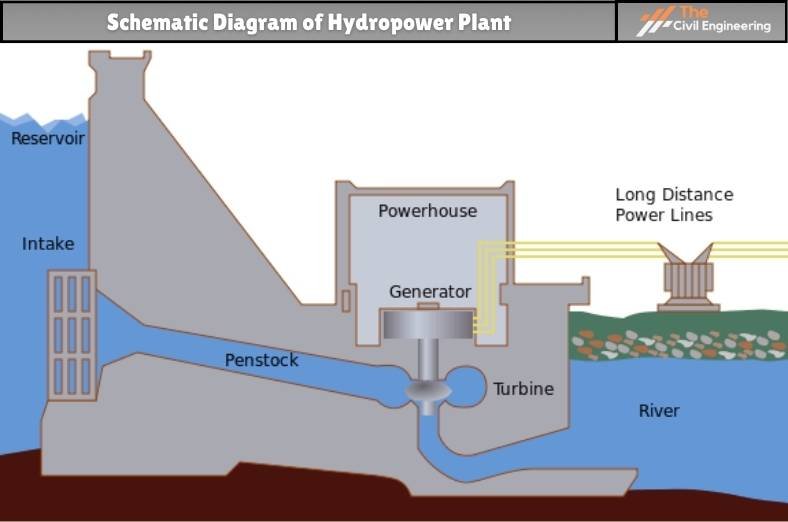
Figure: Schematic Diagram of Hydropower Plant
iii. Water Supply
The dam also serves the function of supplying water both for domestic and industrial use.
The dam is a vital structure that can be used for retaining freshwater, which can be used for human consumption and other domestic purposes.
Water stored by the dam during the wet season can be beneficial, especially in dry periods with a high water shortage.
Likewise, the water stored by the dam can be utilized for various types of industrial work. One of the examples of a dam that has been constructed for water supply is:
1. Corin Dam, a water storage dam in Australia that has a capacity of 19.9*109 gallons.

Figure: Corin Dam, Australia (Water supply Purposes of the dam)
iv. Flood Control
Dams have been used as flood protection structures for centuries.
Flood control dams impound the flood water and store it for use in the future or divert it away. Basically, flood control dams regulate the water level, keep the water temporarily and release it later.
An effective integrated water management plan is prepared beforehand for such dams to efficiently regulate the storage and release of water without any subsequent damage.
One of the prominent examples of such dams is The Tennessee Valley Authority Dams in the U.S.A. It was mainly constructed to help control floods on the Tennessee, the lower Ohio, and the lower Mississippi River.

Figure: Schematic Diagram of Flood Control Dam
v. Inland Navigation
Inland navigation generally refers to ships’ transport through inland waterways such as water canals, rivers, etc.
Various water conditions, such as fluctuating water levels, and changing rivers due to sedimentation and erosion, pose a lot of difficulty in inland navigation.
To overcome such obstacles, dams are built and effectively control the water level and change the course of waterways, facilitating efficient inland navigation.
Inland navigation is an essential means of transport as they permit transporting many goods.
Thus, effective inland navigation with an adequately equipped system of locks, reservoirs, and dams can boost the country’s economic condition.
For example, the T.J O’Brien lock and dam in Chicago.
vi. Recreation
Several fascinating dams have been constructed worldwide, attracting thousands of tourists every year.
Dams also serve recreational purposes such as boating, skiing, picnic, camping, etc.
Moreover, the water stored by the dam serves as the habitat for large species of flora and fauna.
It also aids the growth of flora and fauna in the surrounding area, thereby increasing the scenic appearance of the region.
This has indeed proved to be one of the significant sources of tourist attraction facilitating natural hiking, bird watching, landscape painting, and so on.
Such a rise in recreational activities fosters the flow of economy in the country and thus helps uplift people’s living standards.
Some of the examples of such a dam can be listed as follows:
1. Springbank Dam, London
2. Mitchell Dam, Thames River
3. Centreville Dam, Southwest Oxford
4. Pittock Dam, Woodstock
5. Wildwood Dam, Trout Creek
6. Fanshawe Dam, London
vii. Mine Tailing
Another essential function that a dam serves is mine tailing.
Mine tailing generally refers to the by-products obtained after mining, such as coal extraction, ore extraction, etc.
Such tailings obtained may be in solid, semi-solid, or liquid states. Since these tailings are highly toxic and potentially radioactive, the handling and storage must be done effectively.
The by-products of coal, gold, copper, and uranium also pose a significant environmental risk.
An efficient way of storing such toxic by-products is the construction of a mine tailing dam.
Thus, a mine tailing dam can be used to store such products, thereby mitigating the hazards.
Tailing dams are massive in structure and are ranked as one of the most significant engineering structures in the world.
Some of the examples of tailing dams that have been built across the world can be listed as follows:
1. Syncrude Tailings Dam, Canada
2. ASARCO Mission Mine Tailings Dam, U.S.A
viii. Other Purposes
In general, dams serve as multi-purpose structures.
Primarily dams are used for hydro-power generation and irrigation and for water supply, recreational purposes, etc. Besides these, the water stored by the dam can infiltrate into the ground, recharging the underground water bodies. Hence Purposes of the Dam are many, which bring immediate and dramatic benefits.
| Read Also: What is Pile Foundation? |

