1. Introduction
A building plan may be defined as the graphical or symbolic representation of how a building will look after completion of construction.
It is extensively used by Architects, Engineers, and Contractors in the construction industry.
A building plan can act as a medium of communication between the various parties involved in the construction as it can depict the concept and design of the building to be constructed.
The primary objective of the building plan is to provide an idea of the entire building construction. It is also essential in estimating the total budget required for the construction.
2. Main Purposes of Building Plan
The major purposes served by the building plan can be listed as follows:
a. It helps to visualize the outcome as it depicts how the building will look like upon completion.
b. It acts as a medium of communication between the involved parties. (Building a plan can also help to communicate the ideas to the Client.)
c. It helps to understand the concept, requirements, and scope of works.
d. It can be used for estimating the cost required for the construction work.
e. It helps to make the changes and adjustments easily.
f. It can also help in the selection of suitable materials for the construction.
g. It ensures efficient planning and use of the available space.
h. It helps in the preparation of 3D drawings.
3. Types of Building Plan
The building plans can be divided into the following types:
a. Site Plan
The site plan can be defined as the large-scale drawing that depicts the overall extent of a site for the construction of new structures or the development of the existing structures.
In simple terms, the site plan is the symbolic representation of the arrangement of a building and the associated utilities in a site.
The site plan essentially includes the property lines, existing boundaries, access to the site, and all the existing nearby structures that must be considered during the design.
It represents the top view of a property within a site suitably drawn to scale.
The site plan must also clearly depict the existing household connections, service connections, and utilities such as water supply lines, drainage lines, sewer lines, underground cables, electrical lines, communication cables, etc.
Thus, the site plan includes a set of construction drawings that are necessary for the planning, improvement, and development of a site or property.

The site plan must be made following the existing bye-laws and local development codes. This is because the site plan also serves as a legal agreement for the permission of the construction from the concerned authorities.
i. Suitable Scale for Preparation of Site Plan
The selection of scale for preparing the site plan is mostly done based on the size of the project.
In most cases, the scale of the site plans ranges from 1:500 to 1:200.
It is a common practice to use small scales for large projects and large scales for small projects.
ii. Elements Depicted in a Site Plan
The major elements that are shown in a site plan can be enlisted as follows:
a. Boundary lines and the property lines.
b. Clear outlines of the proposed structures and buildings as well as the outlines of any existing structure.
c. Distance between the proposed structure and other adjoining and nearby structures.
d. The setbacks (i.e. the distance of the proposed structure to the property line.)
e. The parking spaces, parking lots, and driveways.
f. Adjoining and nearby streets and roads.
g. Existing utility and service lines.
iii. Information to be Included in Site Plan
The following information must be included in a site plan:
a. The title block comprising the name of the project, type of the drawing, name of the person who prepared the plan, the status of the project, revision number, and the scale used for the drawing.
b. In case of revisions; notes depicting the changes made must be included. The notes are usually highlighted.
c. The directional orientation i.e. north pointing arrow must be shown.
d. The dimensions of the drawings must be included.
e. The chief materials used can also be included.
f. The property lines or the boundaries of the site along with the adjoining streets and properties must be shown.
g. The location of the site for the proposed construction must be indicated concerning the surroundings.
h. Existing trees, plants, or any environmentally essential elements, or restricted spaces such as public plantations must be included.
i. The parking space with clear dimensions along with the traffic flow and related signs must be shown.
j. The existing streets, roads, pavements along with the easements such as the right of way, right of support, etc must be included.
iv. Additional Information Included in Site Plan
Mostly, when the site of the proposed construction is complex, additional information must be included in the site plan.
The general site plan may be prepared along with the structural plan of the site, site lines, site history, landscaping drawings, existing topography, and geology, etc.
Some of the additional information that can be included in the site plan are as follows:
a. Any existing property or building which has to be demolished must be included in the site plan.
b. The layout of the existing utility lines and service lines such as drainage lines, sewer lines, electricity cables, etc must be shown.
c. The extent of excavation and earthworks necessary including the cutting and filling must be included.
d. The fencings, gates, walls, and other external elements such as fire hydrants, municipal litter bins, etc, if any can be included in the site plan.
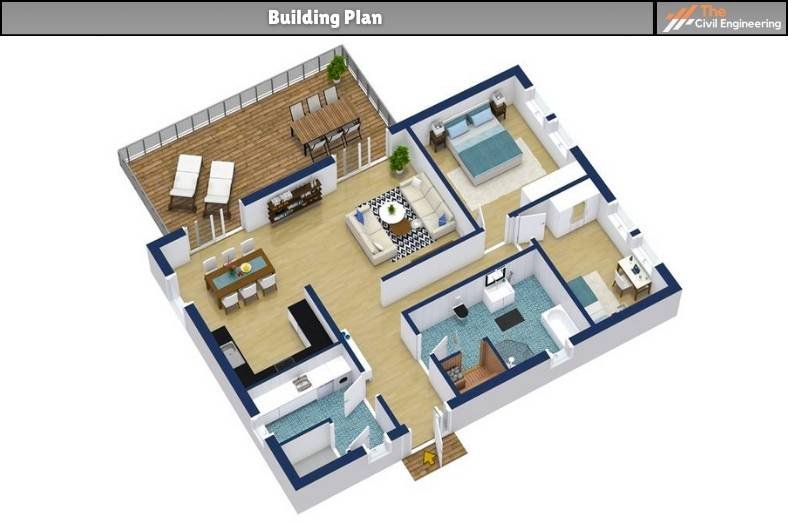
b. Floor Plan
The floor plan can be defined as a drawing sized to a suitable scale such that the positions and orientations of the rooms, utilities, equipment, and furniture are depicted clearly from above i.e. from a bird’s eye view.
The floor plan is the top view of the floor of a building or any structure and is regarded as the most fundamental architectural drawing.
The floor plan is a two-dimensional representation of the floors of a building including the sizes and details.
Designers, Engineers, Contractors, and Architects use the floor plans extensively to represent the arrangement of the available floor spaces within a building.
Precisely, the floor plan can be defined as the vertical orthographic projection of an object in a horizontal plane cutting through the building such that the walls, windows, doors, and other elements such as furniture, stairs, etc within a floor of the building are included.

i. Elements of a Floor Plan
The major elements of a floor plan can be described in brief as follows:
a. Dimensions and Dimension Lines:
Dimensions and dimension lines are the essential elements of a floor plan that represent the size of the items in reality. For example; the length of the doors and windows, size of rooms, etc.
b. Scale:
Scale can range from plan to plan.
Scale refers to the factor that represents the extent to which the whole space can fit on the paper or the screen.
In most cases, the scale ratio of 1/4 inches equal to 1 foot is taken. This indicates that the length of 1/4 inches in the drawing represents a length of 1 foot in reality.
c. Types of Rooms and Accessories:
A typical floor plan represents the walls, windows, stairs, lobby, furniture, etc.
ii. Importance of a Floor Plan
The major importance of the floor plan can be duly listed as follows:
a. It acts as a medium to communicate ideas regarding how the available space can be utilized within the building.
b. It also depicts the scope of works required and the scale of the project.
c. It can be used for interior designing and layout.
iii. Steps in the Preparation of Floor Plan
The main steps involved in the preparation of a floor plan can be listed as follows:
a. Selection of Suitable Area:
First of all, the target area must be decided based on the number of areas required, the required size of the rooms, required shape, etc.
b. Listing of Requirements:
The essential needs and requirements must be listed.
c. Measurement of the Components:
All the essential components such as the walls, doors, windows, and other similar components must be measured or their dimensions must be determined.
d. Drafting of the Plan:
Then, the draft drawing of the proposed structure must be prepared i.e. the framework of the structure must be prepared. Then, the other essential components can be added.
e. Addition of other Elements:
After drafting, additional elements such as furniture, equipment, etc must be added.
f. Checking of the Floor Plan:
Once the drafting of the floor plan is completed, it must be checked with the listed requirements, provided accessibility, etc.
iv. Things to be Considered for Drafting Floor Plan
The things to be considered while designing and drafting the floor plan are as follows:
a. The design must be done such that the usage of the room can be changed in the future if required.
b. The design must be flexible such that any changes in design in the future can be easily incorporated
c. The design of the floor plan must comply with the codal provisions and by-laws.
d. The design of the floor plan must be practical and functional. For example, the bathrooms must be placed at a sufficient distance from the kitchen and dining rooms.
v. Types of Floor Plan
The floor plan can be further divided into the following categories:
1. House Plan:
As the name itself implies, a house plan may be defined as the type of floor plan that essentially comprises the construction drawings indicating the layout of a residential building. The House plan is also referred to as the home plan.
2. Office Plan/Layout:
The office layout is the type of floor plan that represents the top view of the office space or working space within a building.
Different types of office layout that are commonly used are as follows:
a. Cubicle Type Office Plan/Layout:
It is the type of layout in which the partition walls are arranged on three sides of the space to form a cubicle. This type of office plan is mostly used by private companies.
b. Team Type Office Plan/Layout:
Team type of office plan is the type of floor plan in which the entire space is divided into respective departments. The size of each department is determined based on the number of employees in a particular department.
c. Open Type Office Plan/Layout:
It is the type of floor plan in which the entire space is utilized for the seating of employees by placing a lounge seating unit.
3. Garden Plan:
Garden plan is becoming very popular these days. It includes a bird’s eye view of the landscaping and planting arrangements.
4. Fire and Emergency Plan:
Fire and emergency plan is the top view representation of the emergency evacuation plan in the event of a fire.
5. Seating Plan:
Seating plan is mostly used for the construction of auditoriums, theatres, etc. It refers to the top view representation of the seating arrangement within an enclosed space.
vi. Limitations of a Floor Plan
The limitations of a floor plan can be listed as follows:
a. It does not give any information regarding the necessary construction works in detail.
b. It does not provides complete technical information as that required for the construction planners, managers, and engineers. Such as adequate technical information regarding the civil works, plumbing works, etc.
c. Sectional Drawing
Sectional drawing is the symbolic representation of how the building will look if it is sliced in half or is cut along a certain plane.
It is necessary to understand the interrelation between the various components of a building which cannot be interpreted clearly from a simple floor plan.
The imaginary plane along which the building is cut is generally referred to as the section plane.

Section plane is represented utilizing a line comprising of a series of long and short dashes.
In case, more than one sectional plane is present then each of the sectional planes is represented by a particular number or alphabets at either end of the line.
i. Scale for Sectional Drawing
The appropriate scale for the sectional drawing is selected based on the overall size of the building. However, the sectional drawing can include the complete building or a particular part or component of a building, or an assembly of components.
ii. Purposes of Sectional Drawing
The major purposes of sectional drawing can be listed as follows:
a. It is essential to get a clear understanding of a particular section of the building.
b. It helps to understand the internal details of a component or building section. Such as sectional drawings of walls can depict the internal cuts of the gypsum boards, plates, studs, and insulation.
c. It can be used to know about the materials to be used and the assembly of the materials.
d. Elevation
Elevation can be defined as the orthographic projection of a particular side of the building.
Elevation depicts the representation of a side of the proposed building, for example, if the elevation represents the southern side of the building, it is known as the South elevation.
The primary objective of preparing the elevation of buildings is to have an idea about how the particular side of the building will look after it has been completed (i.e. it depicts the finished appearance of the particular side of the building ).
The elevation is drafted based on the vertical height dimensions of the building.

i. Types of Elevation
The elevation can be divided into the following types:
a. External Elevation:
The external elevation is the symbolic representation of the outer side of the building.
It essentially includes the type of finish of the outside of the building, any existing projections, and the floor height.
External elevation can be represented in 2D or 3D view.
It can also provide information regarding the different materials to be used in the various components of the building. There are four types of external elevation:
i. North Elevation
ii. East Elevation
iii. South Elevation
iv. West Elevation
b. Internal Elevation:
Interior elevation is the symbolic representation of the interior portion of a building.
Usually, the interior elevation is used for the designing and construction of the kitchens, living rooms, etc that require the pre-visualization of the interior components.
Interior elevations provide the details of the interior space along with the furniture details, type of lightings, type of paints, etc.
Mostly, internal elevations are represented in 3D view.
e. Landscape Plan
The landscape plan is used to represent the exterior open space of the building from a bird’s eye view.
Usually, the landscape plan is used for the architecturally important structures.
| Read Also: Offsite Construction |
| Read Also: Parapet Wall |