California Bearing Ratio Test is carried out to check the strength of the subgrade of pavement.
By comparing the results of this test with a set of standard curves or values, the thickness of the subsequent layers can also be determined.
It is a type of penetration test and is extensively used in the design of flexible pavements. This test was developed by the California Division of Highways of the United States.
California Bearing Ratio is the ratio of force per unit area required to penetrate a soil mass with a piston of 1.25mm/min corresponding to that required for the penetration of a standard material.
CBR = ( Test load / Standard load ) * 100
1. Apparatus Required
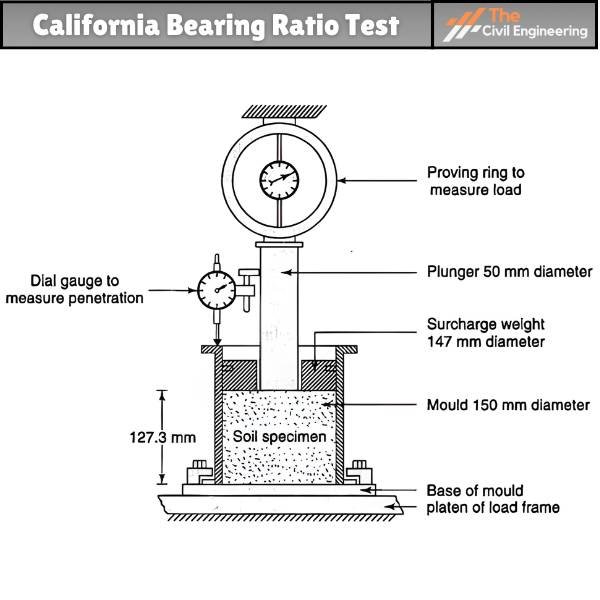
a. Steel: Cutting Collar
b. Dial Gauges
c. Weighs
d. IS Sieves
e. Penetration Plunger ( Diameter: 50 mm & Height: 100 mm )
f. Spacer Disc ( Diameter: 148 mm & Height: 47.7 mm )
g. Loading Machine
h. Cylindrical Mould ( Diameter: 150 mm & Height: 175 mm )
i. Rammers
2. California Bearing Ratio Test Procedure
The procedure for conducting the CBR test is as follows:
1. Prepare the soil sample passing through a 20 mm IS sieve but retained on a 4.75 mm IS sieve.
3. About 4.5kg to 5.5 kg of the sample is mixed with water ( commonly distilled water ). A spacer disc is placed over the base plate, and coarse filter paper is placed over the spacer disc. Then internal oiling of the mould is done, and the mould is fixed in its position. At the top of the mould, a collar is placed.
4. The soil mix is compacted in several layers by static or dynamic compaction.
For Static Compaction: Compacting soil in loading machine ( gradually increasing load ).
For Dynamic Compaction: Compacting soil by rammer ( impact load ).
For light compaction, the soil is compacted into 3 layers by 56 blows with a 2.6 kg rammer from a height of 31 cm.
For heavy compaction, the soil is compacted into 5 layers by 56 blows with a 4.89 kg rammer from a height of 45 cm.
| Light Compaction | Heavy Compaction | |
| No. of layers | 3 | 5 |
| Rammer Weight | 2.6 kg | 4.89 kg |
| Fall | 31 cm | 45 cm |
| Blows | 56 | 56 |
5. The collar is then removed, and the soil is trimmed. The mould is then turned over, and the base plate and spacer disc are removed.
6. The mould is then weighed and bulk density, as well as dry density, is determined.
7. Then, the mould and the surcharge weight are placed on the penetration test machine.
8. The load is applied to the piston such that the rate of penetration is 1.25mm/min.
9. The load readings at penetrations of 0.5,1.0,2.0,2.5,3.0,4.0,5.0,7.5,10 and 12.5 mm are recorded.
10. The mould is detached from the loading equipment, and moisture content is determined.
3. Standard Load Values for California Bearing Ratio Test
| Penetration(mm) | Standard Load(kg) | Unit Standard Load(kg/cm2) |
| 2.5 | 1370 | 70 |
| 5 | 2055 | 105 |
| 7.5 | 2630 | 134 |
| 10.0 | 3180 | 162 |
| 12.5 | 3600 | 183 |
4. Observations During California Bearing Ratio Test
Weight of soil taken =
Weight of surcharge =
Area of the plunger, A =
| Sl No. | Penetration(mm) | Proving dial reading | Load on plunger (kg) | Corrected load | Unit Load |
5. Result of California Bearing Ratio Test
California Bearing Ratio at 2.5mm penetration =
California Bearing Ratio at 5.0mm penetration =
California Bearing Ratio of subgrade soil =
| Read Also: Difference Between Plane and Geodetic Surveying |

