This article clearly describes One Way Slab Vs. Two Way Slab, in other words, carries detailed information about the Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab.
Steel-reinforcement slabs, with thicknesses ranging from 100 to 500 mm, are commonly used for constructing floors and ceilings.
1. One-Way Slab
The one-way slab can be defined as the type of slab in which the ratio of the longer to the shorter span is more than two.
Mathematically;
(Longer Span / Shorter Span) ≥ 2
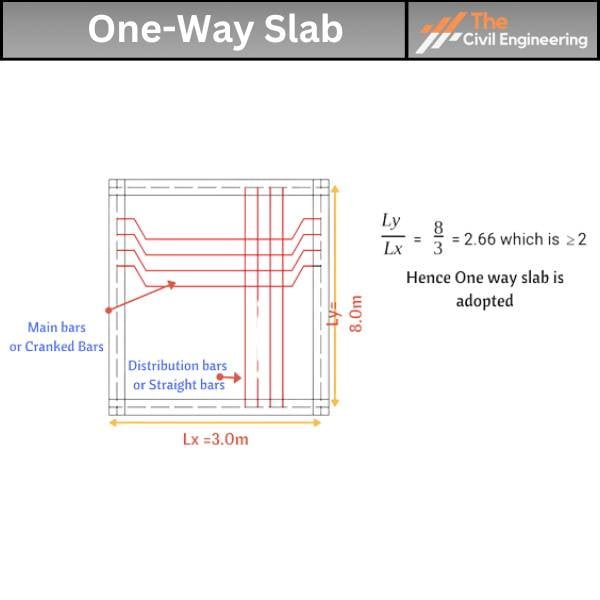
The shorter span of the one-way slab is provided with the primary reinforcement, while the longer span is provided with the distribution reinforcement.
Some prominent examples of one-way slabs are the cantilever slabs, chajjas, and verandahs.
2. Two Way Slab
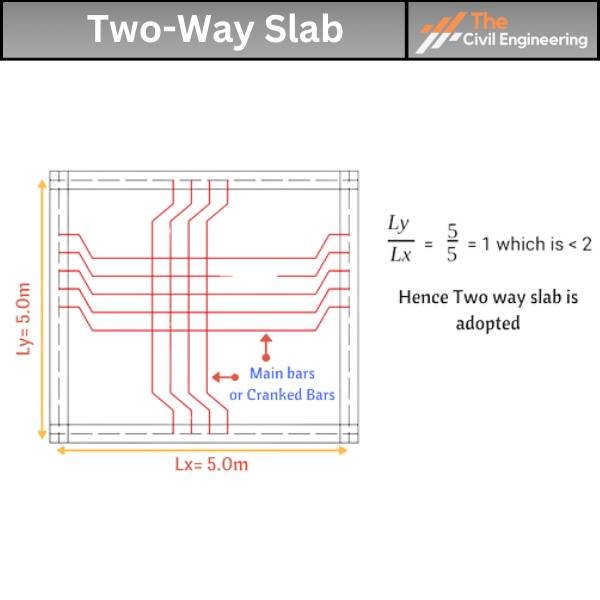
In a two-way slab, the longer to the shorter span ratio is less than two. i.e.
( Longer Span/Shorter Span) <2
The load is carried in both directions in a two-way slab. So, the main bars are provided in both directions.
Two-way slabs are extensively used in multi-story and commercial buildings.
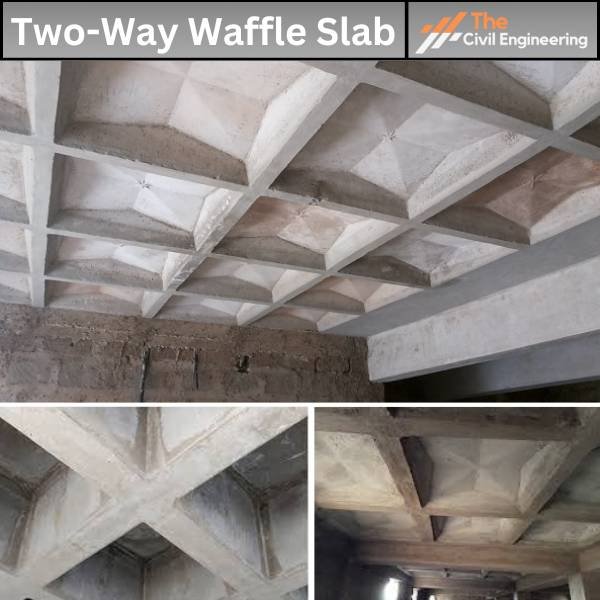
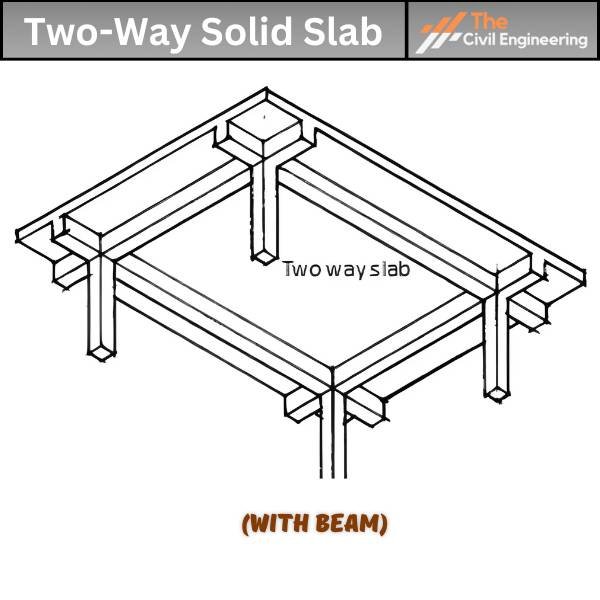
There are three common types of two-way slabs. They are:


| Type of Two-Way Slab | Applications | Span Capability | Rib/Waffle System | Weight | Modular Suitability |
| Two Way Solid Slab (with beams) | Versatile, Large-scale | Wide Range | None | Heavier | Less Suitable |
| Two-Way Waffle Slab (with beams) | Offices, Warehouses, Parking | Moderate Spans | Waffle System | Lighter | Suitable (Low-rise) |
| Two-Way Waffle Slab (with Integral Beams) | Modular Constructions | Larger Spans | Waffle System | Moderate | Suitable |
3. Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab
The difference between a One-way slab and a Two-way slab is as follows:
| Characteristic | One-Way Slab | Two-Way Slab |
| Definition | The ratio of longer to shorter spans is more than two. | The ratio of longer to shorter spans is less than two. |
| Bending moment | Occurs in one direction only. | Occurs in two perpendicular directions. |
| L/B ratio | Greater than 2. | Less than 2. |
| Crank | Reinforcement cranked in one direction (perpendicular to supporting beams) | Reinforcement cranked in two directions (both longer and shorter spans) |
| Primary reinforcement | Provided primarily in one direction (perpendicular to supporting beams) | Provided in both directions. |
| Support | They are supported by a beam on two opposite sides only. | Beams on all four sides support them. |
| Load carrying | The load is carried in one direction perpendicular to the supporting beam. | The load is carried in both directions. |
| Economy | Economical up to a span of 3.6 meters. | Economical for panel sizes up to 6m x 6m. |
| Quantity of steel | Less. | More. |
| Applications | Culverts, bridges, etc. | Residential buildings, water tanks, etc. |
| Read Also: Difference Between Plane and Geodetic Surveying |

