A damp proof course is commonly abbreviated as the DPC.
It is a barrier or obstruction that is primarily designed to prevent moisture from rising by the capillary action.
1. DPC Treatment in Buildings
The DPC treatment in buildings is as follows:
a. Treatment of Foundations Against Gravitational Water
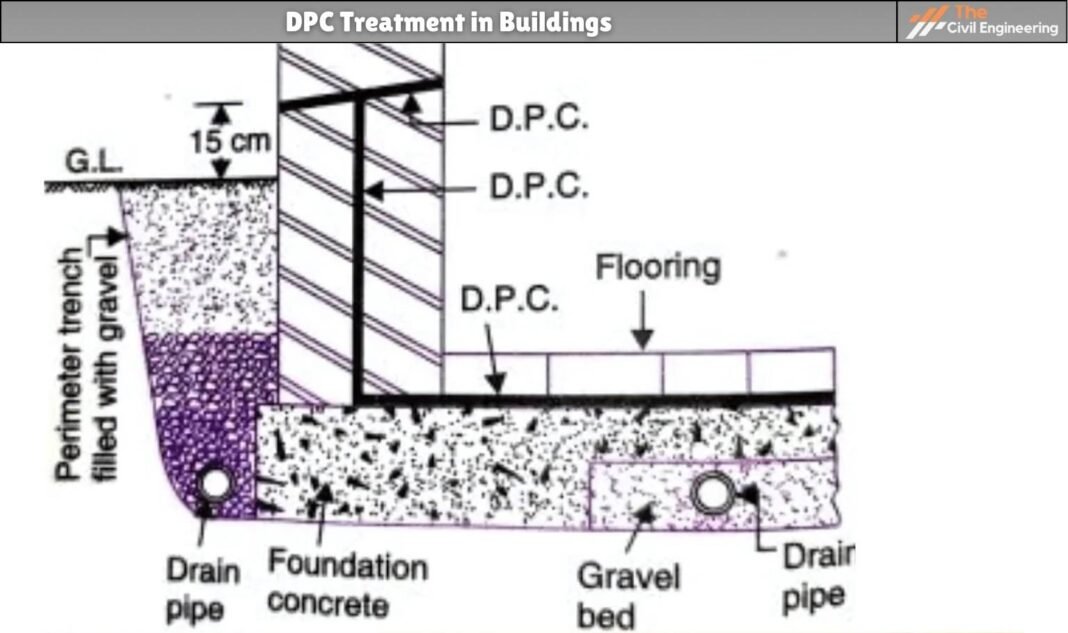
The foundation may receive water percolating from the adjacent ground, and this moisture may rise in the wall. This can be checked by providing an air drain parallel to the external wall.

The width of the air drain may be about 20 to 30 cm. The outer wall of the drain is kept above the ground to check the entry of surface water.
An R.C.C. roof slab is provided. Openings with gratings are provided at regular intervals, for the passage of air. Usual D.P.C. is also provided horizontally and vertically.
b. Treatment to Basements
When basements in damp soils are constructed, three methods may be adopted: (i) Provision of foundation drains and D.P.C.
(ii) Provision of R.C.C. raft and wall slab.
(iii) Asphalt tanking.
(a) Provision of foundation drains and D.P.C
When the basement rests on Roils which are not properly drained, (such as peat soil, etc.) great hydrostatic pressure is exerted and the floor, as well as the wall, receives water continuously, oozing out.
In such a case it becomes necessary to make a trench all around, up to the foundation level, and fill it with gravel, coke, and other previous materials. Open jointed drains may be provided to collect the underground water.
Drainage pipes, embedded in the gravel bed, may also be provided before the foundation concrete.
Horizontal and vertical D.P.C. is provided in the wall as well as foundation concrete. The drain may have a suitable longitudinal slope, ultimately draining the water into a catch drain. Drain pipes under the basement slab may be provided at some suitable intervals.
(b) Provision of R.C.C. raft and wall slab
Where underground water pressure is severe, the drainage system may not solve the problem effectively.
Also, constant pumping out water may be costly. In such a case, floor slabs, as well as walls, may be constructed in a rigid R.C.C. structure. Horizontal and vertical D.P.C. treatment is also provided.
At least 3 layers of bituminous felt are used as D.P.C. Half the brick-thick outer protecting wall is provided at the outer face of the R.C.C. wall slab.
| Read Also: Fire Resistant Construction |
(c) Asphalt tanking
This is adopted when the subsoil water table is not very high. The treatment consists of horizontal D.P.C. in the form of an asphaltic layer 30 mm thick in three coats over the entire area of the basement floor and then extending it in the form of vertical D.P.C. on the external faces of the basement walls. The thickness of the vertical asphaltic layer may be 20 mm, applied in three coats.
The D.P.C. thus functions as a waterproof tank on the external faces of the basement, thus keeping it dry. A 12 -brick thick outer protective wall is constructed. The vertical D.P.C. is taken at least 15 cm above ground level.
A protective flooring of flat bricks on foundation concrete (1 : 3: 6) is provided to protect the D.P.C. from damage during the construction of the floor slab.
c. Treatment of Floors
For locations where ground moisture is not present, subsoil is rammed well, and a 7.5 to 10 cm (thick layer of coarse sand is spread over the entire area under flooring.
Alternatively, stone soling may first be provided and then a 7.5 cm to 10 cm thick layer of lean cement concrete (1: 3: 6 or 1: 4: 8) may be provided under it. Over this base, flooring may be laid.
However, in damp soils, where the water table is near the ground surface, it is essential to provide membrane D.P.C. over the entire area. The membrane may be in the form of mastic asphalt or fibrous asphalt felt.
| Read Also: Timbering of Trenches |
A layer of flat bricks is laid on a cushion of fine sand over D.P.C. to protect it from climate during the construction of the floor slab.
Before laying bituminous felt, a coat of hot bitumen, at the rate of 1.5 kg/m2 is applied over the foundation concrete, to serve as a primer coat.
After laying bituminous felt over it, a finishing coat of hot bitumen, Applied at the rate of 1.5 kg/m2 over the felt.
4. Treatment of walls
For basement walls, a vertical D.P.C. is laid over the external face of the wall. This vertical layer of D.P.C. is laid over the base of water-cement plaster grounded on the external face of the wall.
This vertical D.P.C. is further protected by the external protective wall of half-brick thickness. The vertical D.P.C. should be carried at least up to a level 15 cm above G.L.
Similarly, horizontal D.P.C. in the external wall, extending from the floor, is provided at least 15 cm above G.L.
In the internal walls, D.P.C. is provided on a level with the upper surface of the concrete floor. If two ground floors are at different levels and are connected by an internal wall, the D.P.C. is provided.
5. Treatment of roofs
The methods of providing D.P.C. for flat roofs, copings, and pitched roofs.
This was for the DPC Treatment in Buildings.
2. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, The Civil Engineering (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
Read Also: Damp Proof Course (DPC)
Read Also: Divide Wall