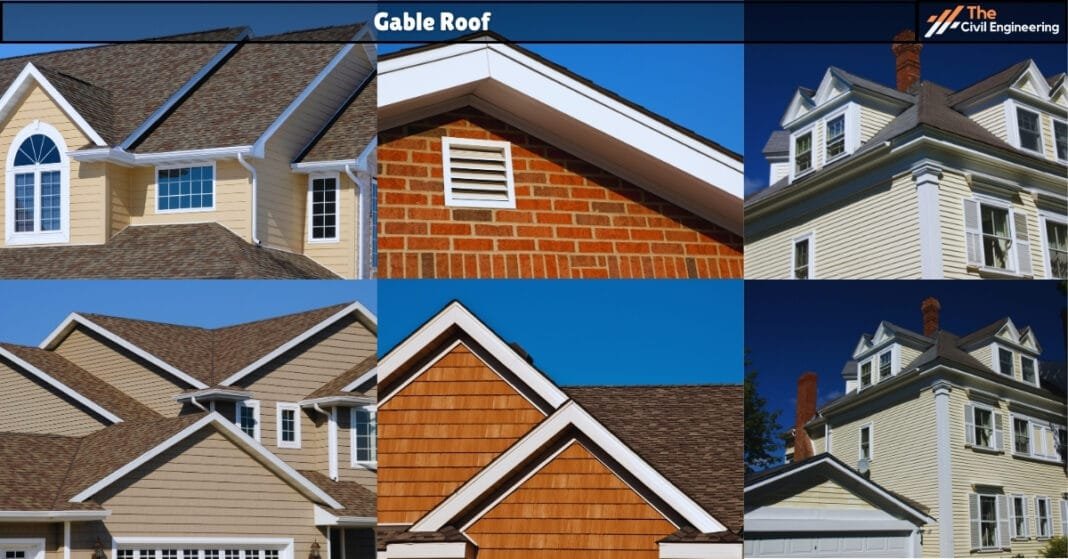
The roof is an important component of any building structure that essentially forms the topmost covering of the structure. It is the structural component that protects the entire structure from the various elements of weather such as rain, frost, hail, etc.
Due to the inevitable nature of roofs in building construction, various types of roofs have been developed and are used all over the world. One such important type of roof is a Gable roof.
A gable roof is the type of roof that is extensively used in regions with cold climatic conditions.
It is also commonly referred to as the classical or Gabled roof. It is made up of two roof sections sloping in opposite directions and placed such that the highest horizontal edges meet to form the roof ridge.
Such an arrangement of the gable roof is achieved using purlins, rafters, and roof trusses.
The height of the gutters and the pitch of the roof can be varied following the requirement.
1. Gable Roof
A gable or gabled roof usually consists of two sides.
These sides have a slope starting from the ridge toward the ends of the roof.
These two sloping sides thus meet and form the end walls that contain a triangular extension. The formed triangular extension is thus known as the gable.
The wall that occurs or exists between the two intersecting sloping sides is also commonly referred to as the A-shaped section.
The size of the sides of the gable roof can be varied based on the building structure.
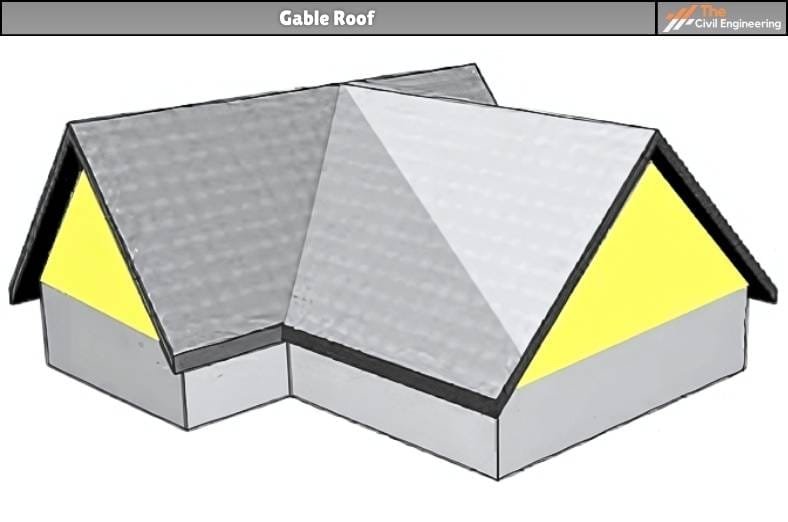
In general practice, two or more gables are used for large residential constructions to add more structure and depth.
The simplicity in the design of the gable roof is one of the most important reasons for its extensive use all over the world.
It also does not require excessive detailing and thus the volume of work and the cost of the overall construction is also greatly reduced.
Generally, the gable roof provided on a church building tower is referred to as a cheese wedge roof and the tower is referred to as the gable tower.
Likewise, if the length of the rafters of the two sections of the roof is different or the pitch is varied, then the gable roof is commonly referred to as the asymmetrical gable roof.
The versatility and flexibility offered by such roofs also make them a common roof choice in many regions throughout the world.
Usually, in regions that are affected by very strong winds and heavy rainfall, the gable roofs are built with a relatively steeper pitch in order. This ensures the prevention of the ingress of the wind.
On the other hand, in the Alpine and the Himalayan regions, the gables are constructed with a shallow pitch.
This is done to ensure efficient support or to withstand the snow load as well as to lower the risk of potential uncontrolled avalanches.
Such design of the gables in the mountainous region also offers great insulation features and prevents heat loss during the wintertime.
2. Historical Development
The history of gable roofs primarily dates back to the Greek civilization.
In ancient Greek times, gable roofs were commonly used in the construction of Greek temples.
The gable roof construction then slowly evolved in parts of Europe and America.
Even today the gable roofs are regarded as an architectural staple in Northern Europe and America. Thus, the advancement of the gable roof commenced.
The building that faced the street with its gable was regarded as the front-building gable. Likewise, the building that has its ridge parallel to the street and faced it with the cullis or gutter was regarded as a side-gabled building.
The front-gabled buildings were extensively used in the German city streets during the Medieval Gothic period.
On the other hand, side-gabled buildings became more popular between the 14th and 17th centuries during the Renaissance period.
The gable roof at that time was highly influenced by Italian architecture.
The front-sided gable again became popular between the beginning of the 19th and 20th centuries, particularly in America.
4. Life Span
The life span of this roofing depends upon the installation technique and accuracy as well as the type of construction material used.
According to statistical reports, the average life span is about 40 years.
The life span of this roofing can be further increased by providing an adequate and appropriate supporting framework.
5. Approximate Cost
In general, the average construction cost of gable roofs has been found to vary from $8 to $16 per square foot.
In this regard, for a 1000 square feet roof, the cost of construction varies from $8000 to $16,000.
6. Construction and Components
A gable roof consists of two sloping sections on the opposite sides of the ridge of the roof.
The sloping sections are placed such that the highest horizontal edges are joined together to form the topmost point which is referred to as the roof ridge.
The roof consists of the pitch and gutters whose size can be varied based on the size of the structure.
It also consists of the ridge board that essentially runs along the peak or the highest point of the roof such that it is parallel with the outside walls. This ridge board further consists of common rafters.
The top of the common rafters is nailed to the ridge boards. The common rafters are placed with the slope in the downward direction and are further nailed to the joints of the ceilings and the outside walls of the building.
The main components of the gable can be listed as follows:
1. Ridge Board
2. Gable Studs
3. Common Rafters
The framing parts of the gable can be listed as follows:
1. Plumb Cut
2. Collar Tie
3. Ceiling Joist
4. Double Top Plates
5. Birdsmouth Cut
6. Tail Cut
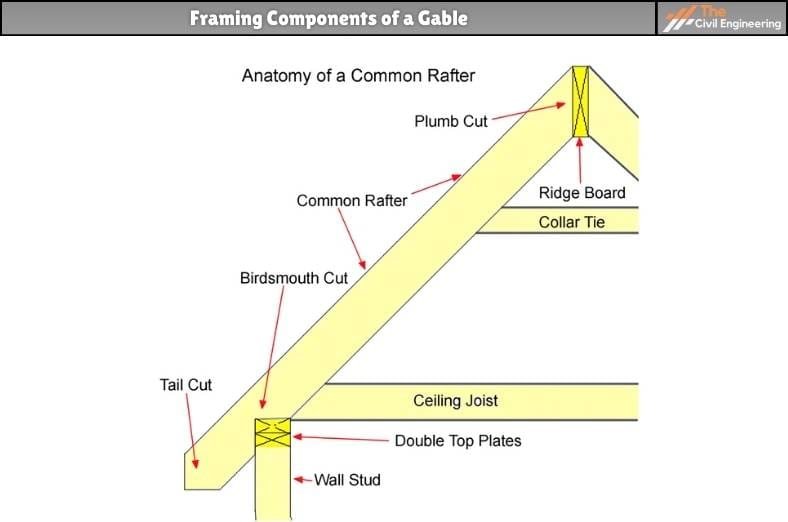
Figure: Framing Components of a Gable
7. Types of Gable Roof
a. Box Gable Roof
This roofing has a triangular extension at each end of the house, with the roof section boxed at the end.
This design is extremely similar to the standard gable roof but distinguishes the triangular section of the design more.
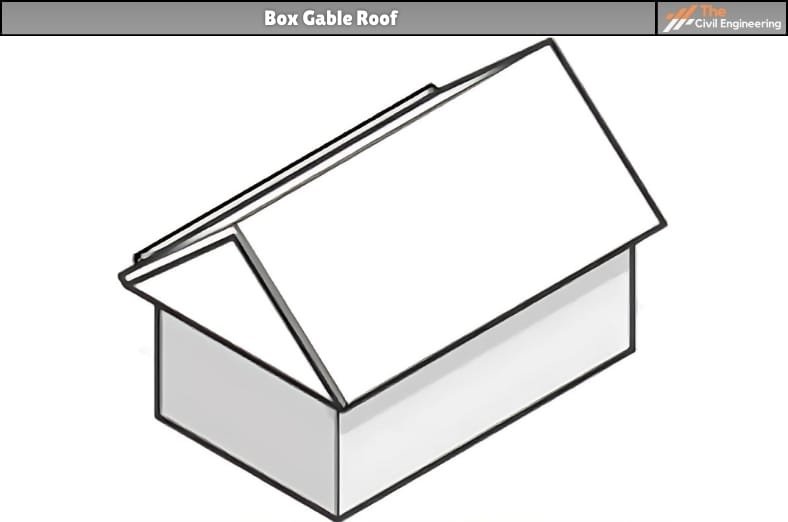
Figure: Box Gable
b. Front Gable Roof
This roofing is placed on the front side of the building structure.
In this type of gable roof, the front door of the building is placed on the front side typically under the gable. It is a commonly adopted roof design, particularly in Colonial-style constructions.
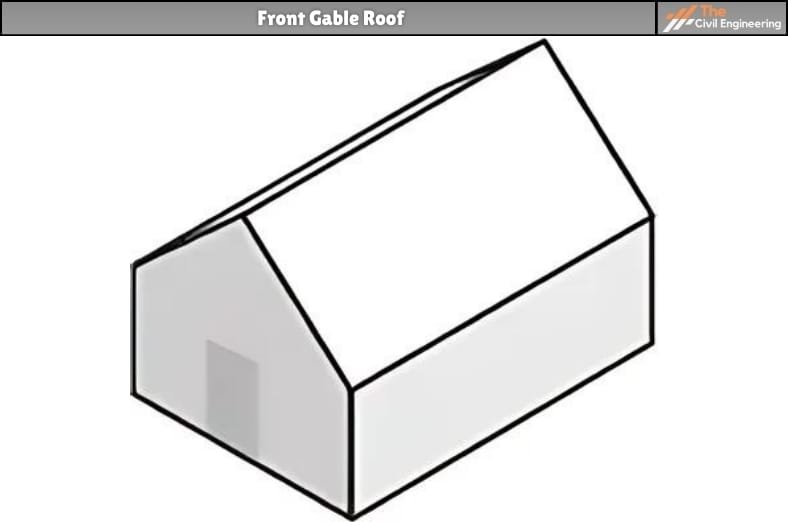
Figure: Front Gable
c. Cross Gable Roof
This roof is made up of two or more gable rooflines.
These gable rooflines are placed such that they intersect each other at an angle, most commonly with the two ridges placed perpendicular to one another.
Usually, the cross-gable roof is regarded as a complex type of gable roof because it has a complex layout due to its complex shape.
It is mostly provided when the building structures have separate wings, a larger porch, or even an attached garage.
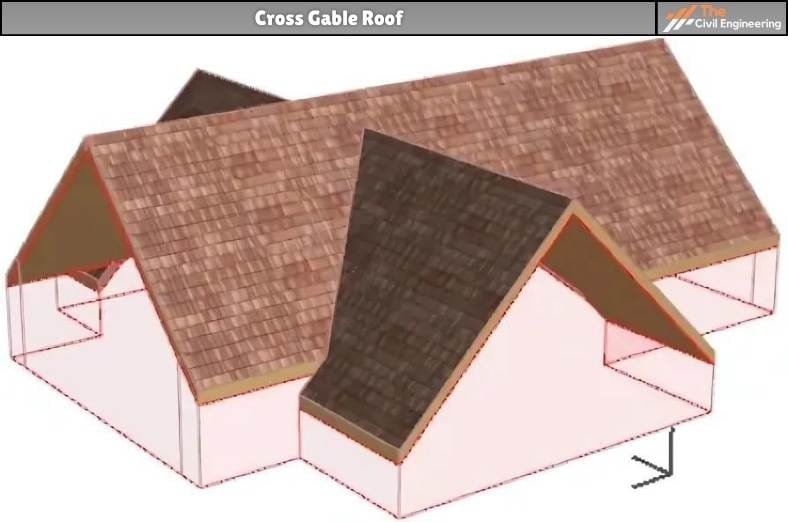
Fig: Cross Gable Roof
d. Gable Roof with Additional Shed Roof
It is a typical alteration for an extension to an existing gable roof is to add a shed roof to the gable roof ridge.
It has become more popular in recent days.
It is also commonly referred to as the hybrid type.
It is commonly adopted in buildings that have the possibility of future extension as this type of roof offers more headroom and space without the need for complete alteration to the structure and preserving the aesthetic appearance at the same time.

Fig: Gable with Additional Shed
e. Dutch Gable Roof
This roofing incorporates the design of both the gable roof and the hip roof.
Thus, It is also commonly referred to as the hybrid roof.
In this type, the gable roof is mostly placed on top of the hip roof. This is done to provide more space within the loft area of the building.
It is a common roof preference in recent days because it greatly enhances the aesthetic appearance of the building as well as provides more space.

Fig: Dutch Gable
8. Advantages
1. Water Drainage System
The sloped sides of the roof provide a certain angle and thus facilitate the sliding off of the water and snow.
Thus, the risk of water leakage inside the structure is greatly reduced.
The reliable drainage system also ensures that the roof can last longer without any potential damage.
2. Easy-to-Build Technology
The gable roofs are based on easy-to-build technology i.e. the gable roof construction is simple and easy.
The method of construction of such roofs is also relatively simple than other alternative of roofs.
3. Additional Space
The design of the gable roof permits more space than other roofing alternatives. The sloped or triangular design of this roofing ensures more space for the owners and the occupants of the building that can be used as the attic space and also regulate proper ventilation inside the building.
4. Affordable and Economical
The construction methodology of the gable roof is also economical and can be completed with limited financial resources.
5. Simple & Wide Range of Construction Materials
The construction materials required for the construction of the gable roof are simple and readily available.
The choice of construction materials is also varied.
Thus, the materials can be selected depending on the preference and budget available.
9. Disadvantages
1. Possibility of Damage by Wind
The gable roof is not desirable in regions that are affected by very strong winds and hurricanes.
Due to the steep pitch, this roof is highly susceptible to wind damage in comparison to other alternative roofs.
The strong wind can create a lot of pressure against the gable thereby causing the roofing materials to peel off.
2. Skilled & Proper Installation
The installation of the gable roof must be done properly by skilled personnel.
The framing technique adopted must also be accurate.
This roofing is at high risk of collapsing if not installed properly.
3. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, The Civil Engineering (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
Read More: Flat Roof
Read More: Earthquake Proof Buildings

