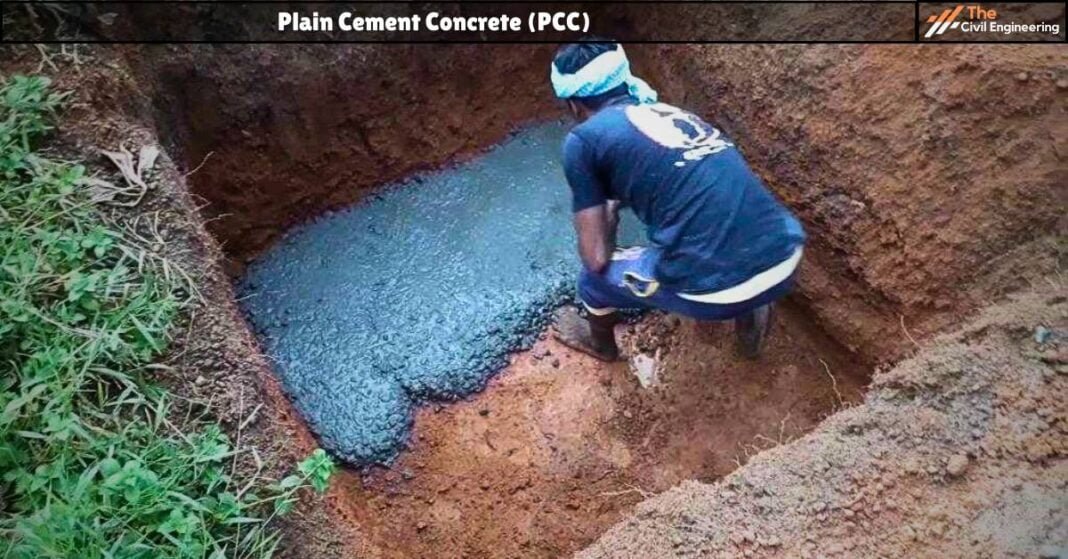
The cement concrete in which no reinforcement is provided is called Plain Cement Concrete (PCC).
✔ It is simply a mixture of cement, sand, and aggregate containing a suitable proportion of water.
✔ It is considerably stronger in compression but weak in tension and shear.

1. Ingredients of Plain Cement Concrete
a. Cement
~ Portland Cement ( commonly OPC) is used in the Plain Cement Concrete.
~ It should have a high degree of fineness.
b. Sand ( Fine aggregate )
~ The sand used should be hard, sharp, and angular.
~ The size of sand should be smaller than 5 mm (i.e. sand passing through a 5 mm square sieve is used).
~ Sand should be free from dust, organic particles, etc.
~ Sea sand is unsuitable for concrete because of its weak bonding capacity.
c. Coarse aggregate
~ It is called aggregate.
~ Aggregates used should be free from dust and foreign materials and also hard to resist enough stresses.
~ Generally, stone ballasts passed through the square sieve of 20 mm and retained in the square sieve of 5 mm are used as coarse aggregates.
~ Aggregates should be well graded so that the voids do not exceed 42%.
d. Water
~ Water should be free from oils, acids, alkalis, salts, and vegetable growths.
~ Water with a pH value of less than 6 is unsuitable for preparing plain cement concrete.
~ Water required for the mix:
Not more than 34 lit – 1:3:6 mix
Not more than 30 lit – 1:2:4 mix
Not more than 27 lit – 1:1 ½:3 mix
Not more than 25 lit – 1:1:2 mix
2. Uses of Plain Cement Concrete
Some of the uses of plain cement concrete are:
a. It is commonly used in the construction of the column foundation, massive gravity dams, flooring, etc.
b. It is used in rigid pavement construction (reinforcement-less rigid pavement).
c. In small-scale canal construction, PCC is used.
d. It is also used in some stone masonry works.
3. Properties of Plain Cement Concrete (PCC)
Some of the properties of plain cement concrete are:
a. Strength
The PCC should have high compressive strength.
The tensile strength should be 8-12% of compressive strength, and shear strength should be 8-10% of compressive strength.
The compressive strength of the PCC depends upon the following:
i. Cement Content
ii. Water Cement Ratio
iii. Method of mixing, placing, compacting, and curing.
iv. Quality of materials used
v. Age of the concrete.
b. Durability
PCC should be able to resist climatic and chemical actions to be durable.
c. Workability
PCC should be highly workable. It should be easy to mix, manage and transport. It should be free from bleeding and segregation.
Workability can be tested with a slump test.
d. Fire Resistance
PCC should be highly resistive towards the fire to prevent problems like firing, spalling of concrete, etc.
4. Preparation of Plain Cement Concrete (PCC)
Plain Cement Concrete preparation includes the following processes:
a. Selection and preparation of ingredients.
b. Mixing of ingredients
c. Transportation and placing
d. Compaction of Concrete
e. Finishing of surface
f. Curing of concrete
a. Selection and preparation of ingredients:
Various ingredients such as cement, sand, aggregate, and water should be carefully selected according to the desired purpose and strength of concrete.
b. Mixing of ingredients:
Ingredients of PCC are adequately mixed with their relative proportion.
Mixing may be of two types:
i. Hand mixing
ii. Machine mixing
i. Hand mixing:
It is the manual process of mixing ingredients by labourers. This method is less suitable because more cement is required than machine mixing.
This method is used when a small quantity of concrete is needed.
The whole mass is mixed dry by working with spades till the entire mass becomes uniform in colour.

Depression is then formed in the centre of the mix, and the required quantity of water is added to this dry mix.
Dry side material is placed on the edge of the depression containing water. It is normally done until the dry mass fully absorbs the water. Care is done not to let the water collapse the banks and flow out.
The wet mass of mortar is then worked with spades to get a mortar of unvarying consistency.
About 25 to 34 litres of water per bag of cement ( 50 kg bag ) is required to make the concrete suitably. Based on the grade of concrete, water requirement differs.
Richer PCC requires less water and vice versa. ( E.g. Not more than 34 lit – 1:3:6 mix. Not more than 30 lit – 1:2:4 mix )
PCC should be prepared in small quantities that can be used before the initial setting time of the cement starts.
(ii) Machine mixing:
When a large quantity of PCC is required continuously at a fast rate, it is prepared by mixing the ingredients in mechanical mixers.

Process of adding materials while mixing:
~ Add half water
~ Add half sand and aggregate
~ Add all the cement
~ Add 1/4 of the water (pour in slowly, running down the drum)
~ Add remaining half sand and aggregate
~ Add the rest of the water to get the required consistency.
~ The drum is then revolved for a sufficient period to form a uniform mixture of the necessary consistency.
~ The mixed PCC is then flowed out for utilization.
c. Transportation and Placing:
The prepared concrete is transported manually in an iron pan or mechanically through a wheelbarrow, buckets, or with the help of the pump.
The media used in transportation depends upon the types and nature of the work.
The placing of concrete means the process of depositing to concrete in its required place and position as fast as possible.

d. Compaction of Concrete:
To remove air bubbles or air voids and to make concrete more dense and compacted, the freshly placed concrete should be compacted with rollers, rods, and vibrators. This process is called the compaction of concrete.
Compaction at a place should be done for a minimum of 5 seconds and not exceed 15 seconds in any condition.
There may be needed for a needle vibrator and a surface vibrator for compaction.
A needle vibrator is generally used to compact the concrete in the small, narrow, and deep areas like a beam, column, etc., and is sometimes used in a flat area, but the surface vibrator is used in compaction of a flat area like road construction.

e. Finishing of surface
Finishing means the removal of irregularities and voids present on the surface.
After concreting, the rough concrete surface is levelled and smoothed during the finishing process.

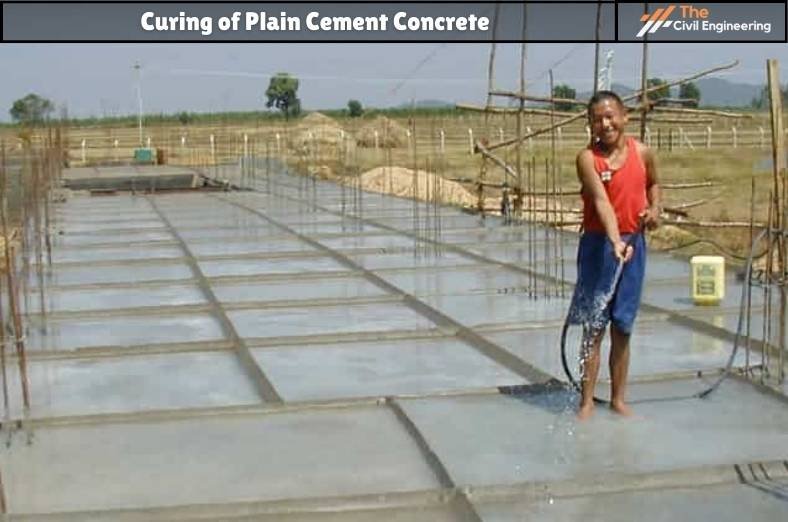
f. Curing of concrete
Wet curing by jute/gunny bags and clothes is done after 2 /3 hours of concrete laying.
After 24 hours, ponding or spraying curing is done for a minimum of 14 days.
In rainy areas, concrete should be covered to protect from water for 24 hours.

5. Dos & Don’ts of PCC Work
Dos
a. When PCC work is to be carried out underground, loose materials from the side of the pits or trenches should be removed.
b. De-watering should be done before PCC work when the water table is high.
d. Shuttering used in the PCC work should have the same size and thickness.
Don’ts
a. Mixing concrete on bare land should not be done.
b. PCC work without formwork should not be allowed.
c. Pouring concrete from more than 1.5 m in height should not be done.
| For curing of concrete: Read |
6. Full Form of PCC in Civil Engineering
The full form of PCC in Civil Engineering is Plain Cement Concrete.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Curing of PCC should be done for? ⇒ Minimum 14 days ⇒ Best to do for 28 days if possible.
2. PCC stands for? ⇒ Plain Cement Concrete
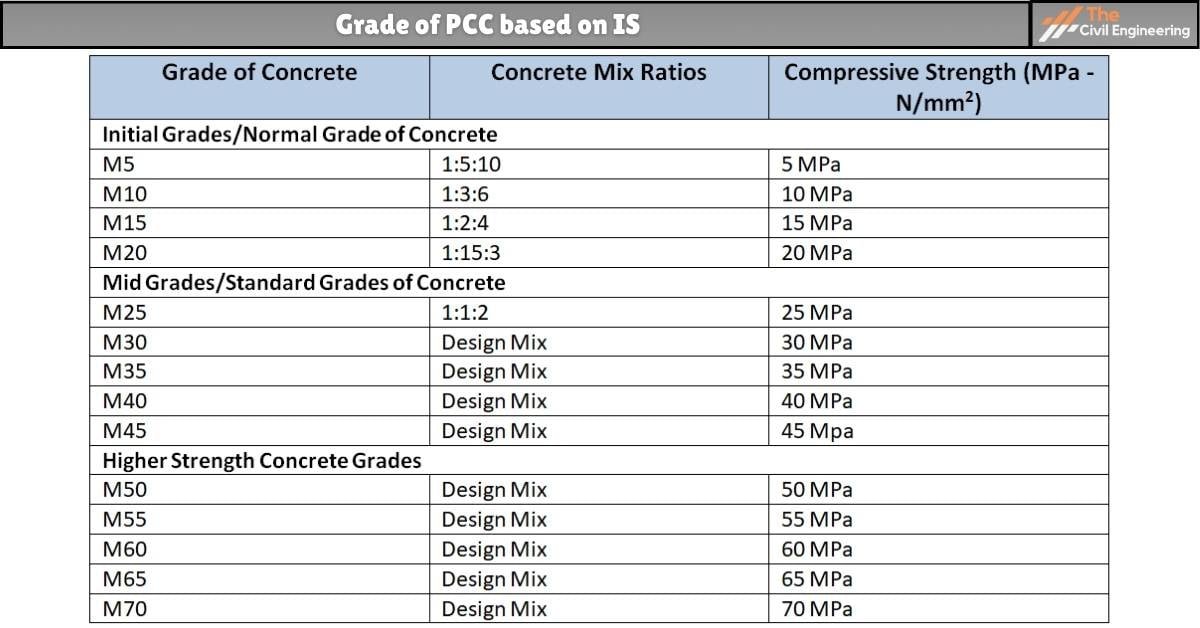
3. Grade of PCC based on IS? ⇒
4. Application of PCC? ⇒ Gardening & Landscaping ✔ Rigid pavement construction ✔ Base preparation for foundation, dams, etc. ✔ Flooring ✔ |
| Read Also: Plastering Work in Construction |
| Read Also: Density of Construction Materials |