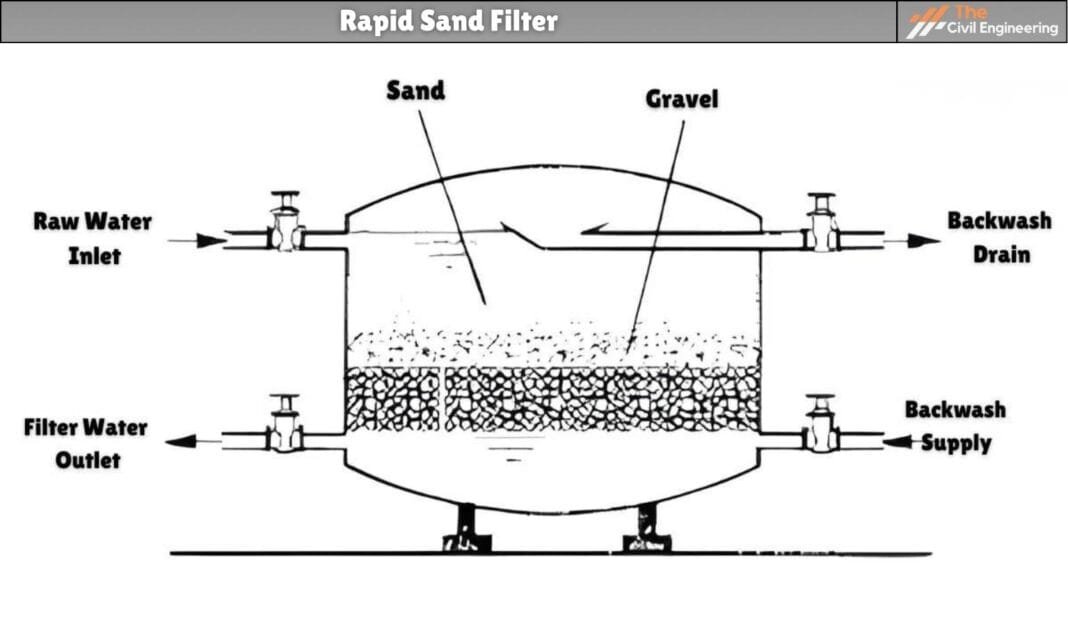
Rapid sand filter is a technique common in developed countries for treating large quantities of drinking water.
It is a relatively sophisticated process usually requiring power-operated, pumps for backwashing or cleaning the filter bed, and flow control of the filter outlet.
A continuously operating filter will usually require backwashing for about one to three days (commonly, in 2 days) when raw water of relatively low turbidity is used. Pretreatment of the raw water, using a chemical flocculation agent in combination with setting tanks is common where turbidity is high. Generally, water is allowed from sedimentation with coagulation to the rapid sand gravity filter.
1. Parts of Rapid Sand Flow
The section of rapid sand filter consists of the following:
a. Enclosure tank
b. Filter media
c. Base material
d. Under drainage system
e. Appurtenances
a. Enclosure tank
Open and watertight rectangular tank constructed of brick or stone masonry or concrete. The depth of the enclosure tank is about 2.5 to 3.5. The surface area or plan area of the tank may vary from 10 to 50 m and the length-to-breadth ratio of the tank is normally kept at 1.25 to 1.35.
The filtration rate varies from 3000 to 6000 lit/hr/m².
b. Filter media
It consists of sand or sand layer 60 to 75 cm thick having effective size (Dio) 0.45 to 0.7 mm. The uniformity coefficient (Cu) of filter media varies from 1.3 to 1.7 and is commonly 1.5.
b. Base material
The filter media is supported on the base material (gravel) of a 45 to 60 cm thick bed. The gravel bed is graded and is laid in different layers each 15 cm thick.
c. Under drainage system
The under-drainage system of rapid sand filter. In rapid sand filter under a drainage system acts for two Purposes;
i) to collect filtered water and
ii) to provide uniform distribution of backwash water.
There are various under-drainage systems for these filters out of which two systems are commonly adopted and are described below.
d. Perforated pipe system
This system consists of a central drain or manifold to which several lateral drains are connected on either side. The lateral drains are provided at a spacing of 15 to 30 cm with perforations. This system is economical and simple to operation. However, more quantity of water at high velocity needs for the backwashing of the filter.
e. Pipe and strainer system
This system also consists of a central drain or manifold to which several lateral drains are connected on either side. Holes are drilled at the top of the laterals and each hole is provided with a strainer. The strainers are either screwed or fixed on the top of the lateral drains. Generally, the spacing of strainers is placed at 15 to 30 cm.
f. Appurtenances
For efficient and proper functioning of filters, certain devices are such during construction known. as appurtenances such as wash water troughs, air compressors, valves, head loss measuring devices, flow regulators, etc.
2. Working and Cleaning of Rapid Sand Filter
At the normal operation stage of a rapid sand filter, only valves 1 and 2 are opened and the rest of other valves are kept closed. Valve 1 (inlet) is opened to allow water from sedimentation with coagulation and valve 2 (outlet) is opened to deliver filtered water to the storage tank.
The water level over the sand bed varies between 1 to 2 meters. Backwashing is usually done when the head loss is reached between 2.5 to 3 m or filter cleaning is done at an interval of 1 to 3 days.
Normally for backwashing, 10 to 15 minutes may require .but for restart operation total time of about minutes may be required. For the backwashing filter, the first step is to close valve 1 and let it decrease the water level to the edge of the wash water troughs.
The next step is to close valve 2, now open valve 6 to permit compressed air for about 2 to 3 minutes in the upward pe direction surface scum will break up and loosen the dirt. Close valve 6 and open valve 4 to permit wash water.
Open valve 3 to discharge dirty wash water through the wash water drain. Now close valve 4 and valve 3 and allow a certain time to settle materials to the surface of the sand. Now open valve 1 slightly and open valve 5 for a few minutes to discharge filtered water to wash the water drain.
Finally close valve 5 and open valve 2. Now filter can be operated at a normal filtration rate.
4. Efficiency of Rapid Sand Filter
1. It is excepted that bacteria removal efficiency is about 80 to 90%.
2. Turbidity of water can remove the extent of 35 to 40 ppm.
3. These filters are highly efficient in color removal i.e. below 3 on the cobalt scale.
5. Advantages of Rapid Sand Filters
The advantages of this technology are that it is a proven technology, effective in removing suspended solids and that it requires a minimum land area for construction and operation Compared to slow sand filters.
6. Disadvantages of Rapid Sand Filters
Rapid sand filters have high capital and operation costs, which may be increased further if there is a need for the pretreatment of raw water.
The technology uses energy for pumping and requires a relatively high degree of training for the plant operator.
3. References1. Content Filter & Authenticity Checking Team, The Civil Engineering (Our team checks every content & detail to maintain quality.) |
Read Also: Slow Sand Filter
Read Also: Water Treatment Process