1. Introduction
Septic tanks are usually underground chambers and are commonly constructed using concrete, steel, fibreglass etc. The design of the septic tank is very essential for the proper disposal of night soil and wastewater disposal.
Septic tanks can range in size from just five hundred gallons for small simple septic tank systems to thousands of gallons for large septic tank systems.
Commonly, for the residential purpose, the size of the septic tank adopted is one thousand to fifteen hundred gallons.
The septic tank may be designed as a single chamber or multiple chambers depending upon the requirement.
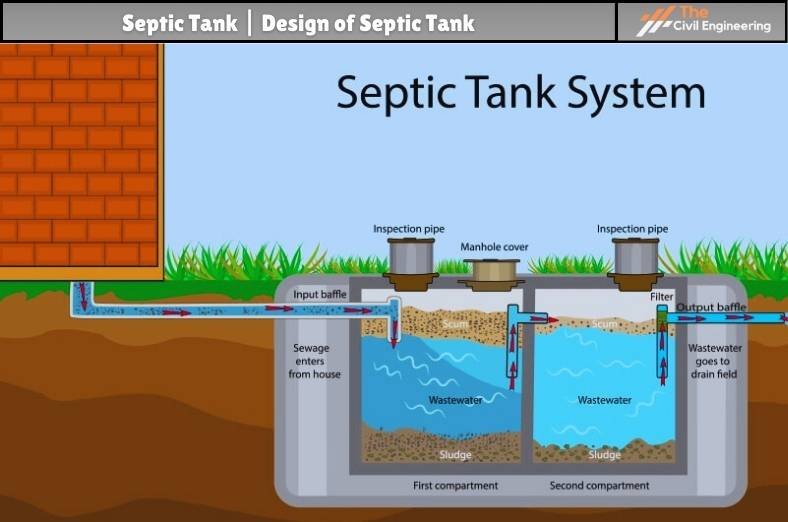
In general practice, the septic tank consists of two distinct chambers namely the treatment chamber and the final chamber.
One inlet is provided in the treatment chamber and one outlet is provided in the final chamber. The outlet is provided at a lower level than the inlet to ensure the rapid flow of the effluent without any obstruction in a particular direction only.
The treatment chamber is the working chamber of the septic tank where most of the biochemical process occurs.
2. Components of Septic Tank
1. Working Chamber:
The working chamber is the main working space where the anaerobic decomposition as well as the settling of the sewage particles takes place.
2. Inlet Pipe:
The inlet pipe is provided in the septic tank to pass the collected wastewater and the night soil inside the tank.
3. Baffle Walls:
The baffle wall is generally provided near to the inlet pipe. Baffle wall serves as the breaker for the incoming sewage. Such wall also prevents the congestion or blockage of the outlet pipe by the overflow of the effluent.
4. Outlet Pipe:
The outlet pipe is provided in the septic tank to pass the collected effluent to the drain field for efficient disposal.
The outlet pipe is always provided at a level lower than the inlet pipe.
5. Roofing Slab:
The roofing slab is the top cover that is provided to the septic tank.
In general practice, roofing slab comprises of RCC slabs and may be circular or rectangular.
6. Ventilation Pipe:
The ventilation pipe of the septic tank is also commonly referred to as the Air Vent.
The main objective of providing the ventilation pipe is to facilitate the circulation of air inside the tank and to prevent foul odour.
It is usually made up of cast iron or asbestos.
At the top of the ventilation pipe, a wire mesh is provided to check the entry of flies, mosquitoes and other insects.
3. Design of Septic Tank
The design of septic tank mainly depends upon the number of users expected to make use of it.
In this regard, the capacity of the sludge tank mainly depends upon the number of users and the sludge removal interval.
It is a general practice to remove the sludge every two years.
The liquid capacity of the septic tank is usually taken as 120 litres to 170 litres per head.
For small residential use, 120 litres per head is generally adopted as the liquid capacity of the tank.
The chamber of the septic tank is mostly made up of brick wall with cement mortar.
The wall thickness should not be less than 9 inches and the foundation floor must be made up of cement concrete of mix 1:2:4.
It must be noted that both the inside as well as the outside faces of the wall and the top layer of the floor must be plastered with a minimum thickness of 12mm i.e. one and a half-inch thick.
The mix of the cement mortar for the plastering work should be 1:3. Some water-resistant admixtures may be added to the mix.
The floor of the septic tank must be designed such that it consists of a slope of 1:10 to 1:20 towards the inlet. This is done to ensure efficient collection and removal of the sludge.
The design criteria of the various components of the septic tank can be duly listed as follows:
1. Detention Period:
The detention period for the septic tank is taken as twenty-four hours. In the design of the septic tank, the rate of flow of the influent is taken equal to the rate of flow of the effluent.
2. Dimensions of the Septic Tank :
The design of the septic tank must be done in such a way that the width of the tank is not less than 750mm. The length is usually taken as two to four times the width and the depth is taken as 1000 to 1300 mm plus 300mm to 450mm is taken as the freeboard. The minimum capacity of the tank is taken as 1 cubic meter.
Width = 750mm(min)
Length = 2 to 4 times width
Depth = 1000 to 1300mm. (min below water level) + 300 to 450mm free board
Maximum depth = 1800mm + 450 mm free board
Capacity = 1 cubic meter (10 cubic feet) minimum
3. Inlet and Outlet Pipes:
For the inlet wall, a T pipe or an elbow with a minimum diameter of 100 mm must be used and it must be submerged to a depth of 250 to 600 mm below the liquid level.
For the outlet wall, a T pipe or an elbow with a minimum diameter of 100mm must be used and it must be submerged to a depth of 200 to 500mm below the liquid level.
4. Baffle Wall:
The inlet baffle wall is provided near to the inlet region.
If the length of the wall is L then the baffle wall is placed at a distance of L/5 from the wall.
The thickness of the baffle wall is kept between 50mm to 100mm.
5. Roofing Slab:
The thickness of the top slab must range from 75mm to 100mm based on the size of the tank.
For the circular cover, the minimum diameter must be kept as 500mm and for rectangular cover, the minimum size must be kept 600*450mm.
6. Ventilation Pipe:
The diameter of the ventilation pipe should not be less than 50mm and not more than 100mm.
The ventilation pipe should extend at least 2m above the ground level.
4. Numerical
Design of Septic Tank for 20 Users
@120 liters per user = 0.12 X 20 =2.4cum
Take liquid depth as 1.3meter.
Therefore Floor area of the tank = 2.4/1.3 = 1.85m2
Taking length as 2.5times the breath
L X B=1.85
2.5B X B = 1.85
B = √(1.85/2.5) = 0.86 say 0.9m
Therefore, the dimension of the tank is 22.5 X 0.9m
British Standard Calculation:
British standard given following formula calculate the wastewater flow for a septic tank.
C=A + P (rq + ns)
Where,
C – Capacity in litres
P – Number of People
A – 2000 Litres as constant
r – Detention period of Sewage in Days
q – Sewage Flow in litre per day
n – Number of years
s – Sludge accumulation in litres per person/year
Simplification of (rq + ns) = 180 Litres (Supposed)
We can Rewrite the formula C=A + 180 P
C = 2000 + (180 × 5)
= 2900 Litres
| Read More: Structure Relocation |
| Read More: By Law and Code |


