In this article, we will discuss soil erosion.
1. Introduction
Soil erosion is the detachment of individual soil particles from soil mass transport by erosive agents such as air, water, and deposition of transported particles after the energy for transport is insufficient.
Soil erosion agents
• Wind: by wind velocity
• Water
a. Rainfall
b. Surface runoff
c. Subsurface runoff
d. Glacier (causing landslides)
Gravity: Mass soil movement in forms of landslide, landfall, debris (mudflow), creep (movement of large soil particles by rolling and sliding).
2. Factors Affecting Erosion by Water
a. Climatic factors
Rainfall characteristics: major
Rainfall intensity<infiltration rate: not much erosion
The higher amount and intensity: higher erosion and higher runoff,
Frequency: frequent rainfall> maintaining soil moisture, high runoff, and erosion
Uniform rainfall throughout the year: less soil loss
Wind velocity
Atmospheric temperature
b. Soil characteristics
Infiltration rate
Infiltration rate>rainfall intensity: no runoff
Soil cover providing resistance
More moisture content: high runoff
Compacted soil: less erosion
High permeability: less runoff
Infiltration rate: depends on soil texture
Larger particle size: less erosion
c. Vegetation
Obstruction to flow reducing velocity and erosion
Thicker vegetation cover: less erosion Interception of rainfall reducing surface runoff and erosion
Roots reducing runoff and erosion
Water loss through transpiration
d. Topography
Slope: higher slope, more erosion
Slope length: increasing the velocity of flow
Slope shapes (concave slope: flatter at the bottom, steeper at top, mainly deposition and convex slope: Steepness increase towards the bottom, removal)
3. Types of Soil Erosion Due to Water
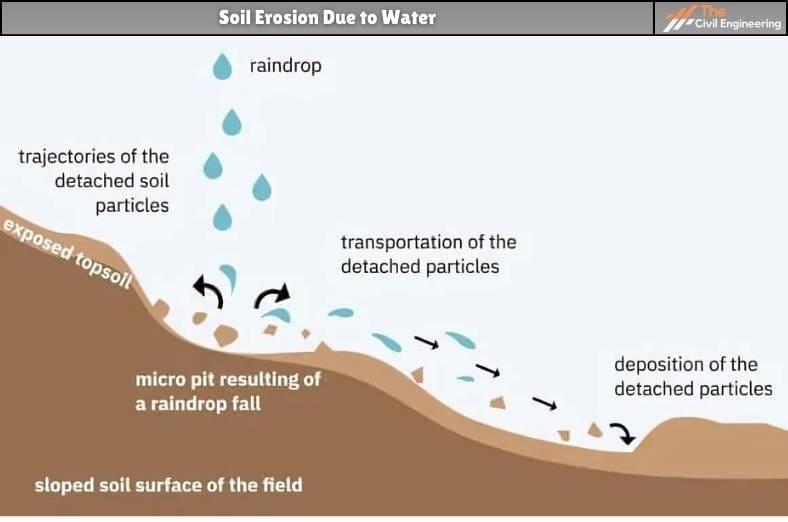
a. Raindrop or Splash Erosion
Raindrop or splash erosion is the erosion of small soil particles caused by the impact of raindrops on wet soils. Soil splash occurs in two ways: detachment of foil particles due to falling raindrops and transportation of the soil particle.
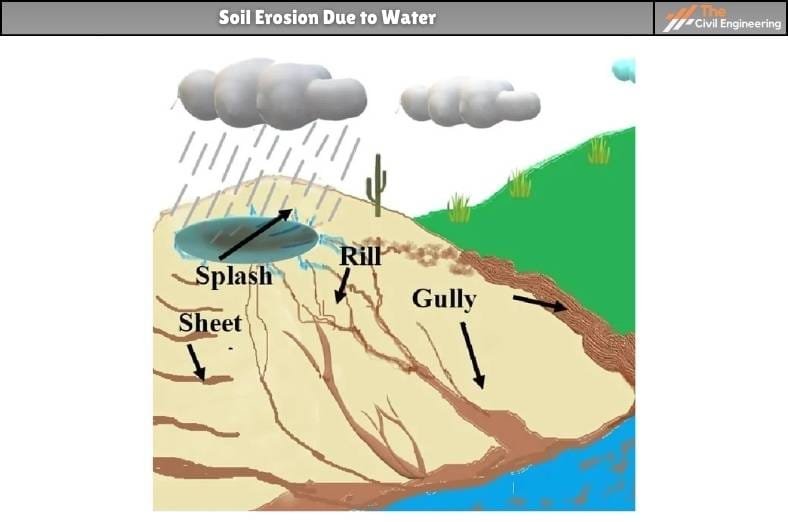
b. Sheet Erosion
Sheet erosion is defined as the removal of a thin uniform layer of topsoil by runoff water. In reality, sheet flow is carried out by a very small definable channel called inter-rills. The soil particles detached by the impact of raindrops are carried through the inter-rills by a very thin layer of overland flow.
This type of erosion occurs on smooth land surfaces and on uniform slopes. Although the total amount of soils removed in a storm by sheet erosion is small, the contribution becomes significant over a long period of time as it transports the soil detached by raindrop splash.
c. Rill Erosion
Rill erosion is the removal of soil by the concentrated sheet flow. Prolonged occurrence of soil erosion through inter-rills, leads to widening of inter-rills and formation of small channels. These rills carry both the overland flow from inter-rill areas and direct flow. The soil erosion is high from the channelized flow.
d. Gully Erosion
Gullies are relatively permanent steep-sided watercourses. Gully erosion is the advanced stage of rill erosion. Gullies are formed when there is more continuous erosion from rills and also due to the subsurface soil erosion.
e. Stream Channel Erosion
Stream erosion is the removal of stream banks soil by water. It is caused by the force of running water or by scouring (removal of sediments from a stream bed running water) or by undercutting.
Read More: Standard Proctor Test of Soil
Read More: Consolidation Test on Soil