| In this article, we will discuss 7 types of pile foundations with suitability, benefits, and uses. |
What is a Foundation?
Foundation is the substructure that transfers the load from the superstructure to the soil beneath. It is responsible for the stability of the whole structure.
There are 2 types of foundation naming shallow foundation and deep foundation.
It is suitable to construct a shallow foundation when the surface soil has acceptable or adequate bearing capacity.
On the other hand, a deep foundation is suitable when the surface soil is weak and thus the foundation has to be taken deep down where the soil has adequate bearing capacity.
An example of a deep foundation is the pile foundation.
1. What is Pile Foundation?
A pile foundation is a type of deep foundation that comprises a long, slender column used to transfer the load coming from the superstructure to the lower-lying ground through skin friction or end bearing mechanism.
In general, a pile foundation is a long cylinder usually made up of steel or concrete and driven deep into the ground to act as a base or support to the structure built on it.
✔ Sometimes, timber is also used as a pile foundation.
✔ Pile foundation is mostly used when the upper soil layer is weak and does not have sufficient bearing capacity to withstand the imposed load by the structures.
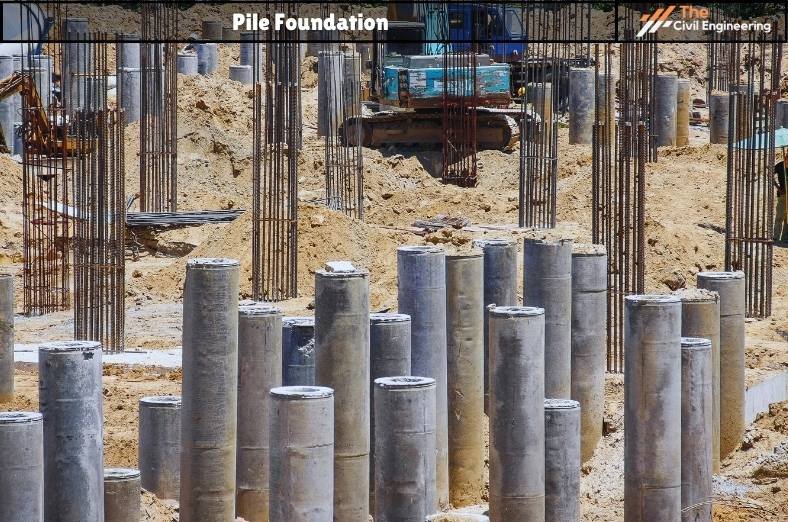

2. Suitability of Pile Foundation
It is desirable to use pile foundations in the following cases:
1. The surface soil layer is weak and cannot resist the load of the structure and undergoes excessive settlement.
2. When the structure to be constructed consists of very heavy concentrated loads such as in the construction of high-rise buildings, water tanks, bridges, etc.
3. When the groundwater table is relatively high.
4. When the construction has to be done on the riverside, river bed, or seashore where there is an increased risk of scouring.
5. When other types of foundations are not feasible or expensive.
6. When a canal system or deep drainage structure exists nearby the construction site.
3. Advantages of Pile Foundation
Some of the benefits of using a pile foundation can be listed as follows:
1. It is advantageous when the foundation has to be drilled through hard rocks or tough surfaces.
2. It is long-lasting.
3. Pile foundation can be pre-ordered as well as customized according to the need.
4. It is desirable even for wetland constructions and for all sizes of land construction.
4. Factors Affecting Selection of Types of Pile Foundation
The factors that affect the choice of the types of pile foundation are listed as follows:
1. Properties of soil.
2. Availability of construction materials.
3. Types of the load imposed.
4. Length of pile needed.
5. Depth of water table.
6. Type of structures existing nearby.
7. Budget available and durability desired.
8. Availability of driving equipment.
9. The intensity of groundwater flow.
5. Types of Pile Foundation
Pile foundation may be classified based on various factors which are discussed below:
A. Based on Function or Use
Depending upon the function or purpose served, pile foundation may be classified as follows:
i. Sheet Piles
Sheet piles are the type of piles that are primarily used for providing lateral support and resisting the lateral pressure generally from loose soil, the flow of water, etc.
✔ Primarily, such type of piles is used for the sheeting of trench, protection of shore, cofferdams, etc.
✔ Vibratory hammers are commonly utilized in the installation of sheet piles. If the soil is too hard then impact hammers can be used for installation.
✔ Sheet piles are made up of steel, but can also be formed of reinforced concrete or timber.
“One of the limitations of sheet pile is that it cannot be used for providing vertical
support to the structure.”
Some Purposes of Sheet Piles are:
1. Retaining the loose soil around the foundation trenches.
2. Constructing retaining walls.
3. Constructing erosion protection structures.
4. Confining the soil and isolating the foundation from the adjacent
soil layers.
1. Selection of Sheet Piles
The selection of sheet piles depends upon the following:
a. Type of work ( permanent or temporary )
b. Site conditions
c. Type of protection required
d. Depth required
e. Bending moment induced.
2. Uses of Sheet Piles
Some uses of the sheet piles are:
a. Used in the construction of seawalls and bulkheads.
b. Used in the construction of seawalls and bulkheads.
c. Used as barriers to groundwater flow.
d. Used for retaining the loose soil around the foundation trenches.
3. Types of Sheet Piles
There are four types of sheet piles that are commonly used.
a. Timber Sheet Piles
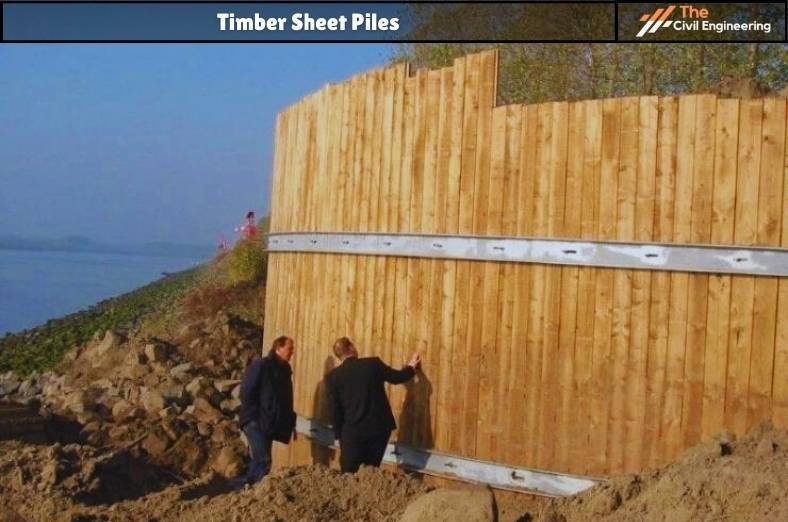

✔ Commonly used for temporary structures and short spans.
✔ Able to resist light lateral loads.
✔ Timer sheets are connected by tongue and groove joints.
✔ Requires preservative treatment of the timber sheet piles before application.
✔ Not suitable in the strata consisting of gravel and boulders.
b. RCC Sheet Piles
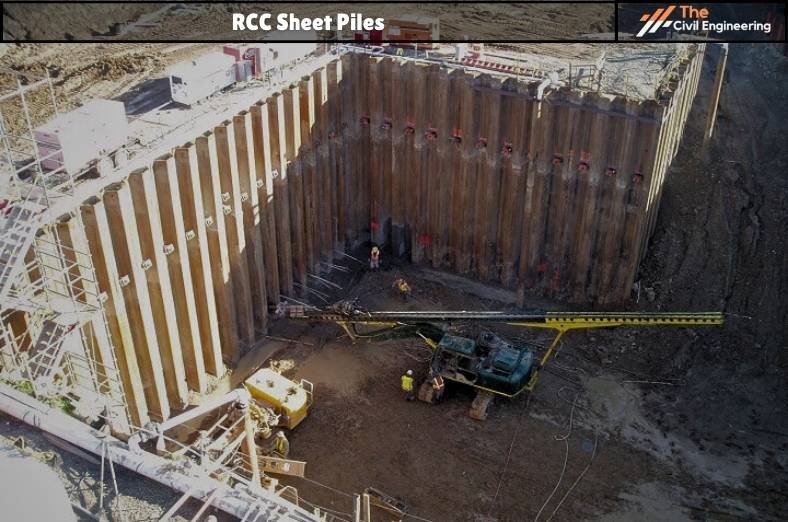

✔ These piles are formed utilizing precast concrete members which are connected together by tongue and groove joints.
✔ Generally utilized as a permanent structure in river embankments, canals, and other marine structures.
✔ Toe of the Piles: Oblique face to facilitate easy driving and interlocking
Head of the Piles: Finished off by casting a capping beam.
c. Vinyl Sheet Piles
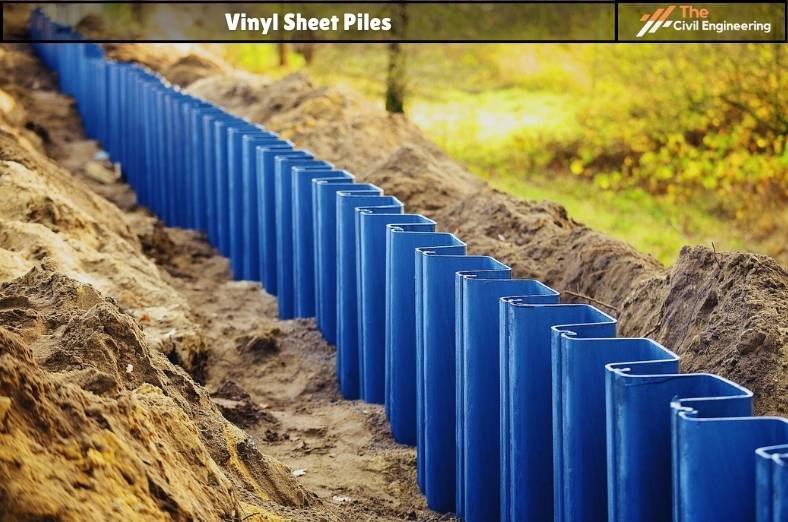

✔ Suitable for both temporary and permanent constructions.
✔ Best alternative of steel, wood, and concrete piles.
✔ Highly durable and corrosion resistive when exposed to seawater, where no oxidation occurs.
d. Steel Sheet Piles
✔ Steel piles are commonly utilized because of the following reasons:
a. High resistance to driving stresses
b. Excellent water-tightness
c. Length can be easily increased by welding or bolting.
d. Durability can be increased by corrosion protection measures such as coating and cathodic protection.

✔ These piles are generally interconnected by interlocking.
✔ Different forms of steel sheet piles are:
a. Normal sections
b. Composite sections
c. Box sections
d. Straight web sections
4. Advantages of Sheet Piles
a. Reusable
b. Recyclable
c. Can be used in both temporary and permanent constructions.
d. Available in a wide range of shapes and sizes.
e. Requirement of less maintenance.
f. Can be installed in very less time.
5. Installation of Sheet Piles
| Read Also: What is Road Maintenance? : 4 Types, Precautions & Factors Affecting Road Maintenance |
ii. Load Bearing Piles
A load-bearing pile transfers the vertical loads of the structure to the underlying soil by either an end-bearing mechanism or by frictional mechanism.
Based on the load transfer mechanism, load-bearing piles can be further classified into the following:

Figure: Types of Load Bearing Pile
a. End Bearing Piles
✔ The end-bearing piles are driven into the ground such that the bottom end tip of the pile rests at the intermediate layer between the weak soil layer and the strong soil layer.
✔ The bearing capacity of such a pile can be easily determined by multiplying the area of the bottom tip of the pile and the bearing capacity at that particular depth of soil where it rests.
Then, considering a certain factor of safety, the diameter of the pile can be determined.
b. Friction Piles
✔ A friction pile is the type of load-bearing pile that transfers the load to the soil by the friction mechanism between the surface of the pile and the surrounding soil layer.
✔ Friction force can be developed along the entire length of the pile or a certain length of the pile depending upon the strata of the soil.
✔ Unlike, end-bearing piles, in friction piles, the entire pile surface functions to transfer the loads from the superstructure to the soil.
✔ The capacity of friction piles can be determined by multiplying the surface area of the pile by the friction force developed per unit area. A certain factor of safety must be considered while designing friction piles.
iii. Soil Compactor Piles
Sometimes, it may be necessary to compact the soil to increase its bearing capacity.
Piles used for such purpose of increasing the bearing capacity of the soil are known as soil compaction piles.
The sand compaction pile is an example of the soil compactor pile.
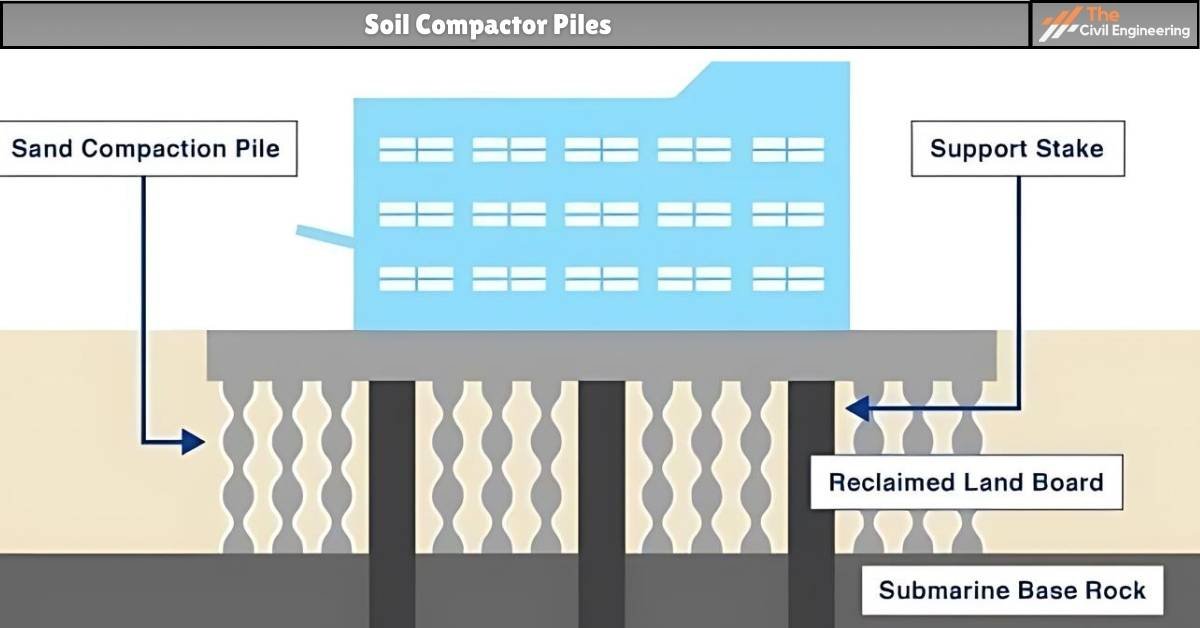
Figure: Soil Compactor Pile
B. Based on the construction method or construction material used
Depending upon the method of construction of the pile foundation and the materials used; pile foundations may be classified into the following:
i. Timber Piles
Timber piles generally refer to the type of pile foundation that comprises timber as the material of construction.
✔ Timber piles are mostly placed under the water level and can be rectangular or circular.
They have a long life span of approximately 30 years.
✔ During the design of timber piles, commonly the diameter is kept between 12 to 16 inches and the length is taken as 20 times the top diameter or less.
Such piles can withstand loads as high as 15 tons to 20 tons/pile.
✔ Usually, fish plates are attached or bolted on the side of the timber piles to gain additional strength.
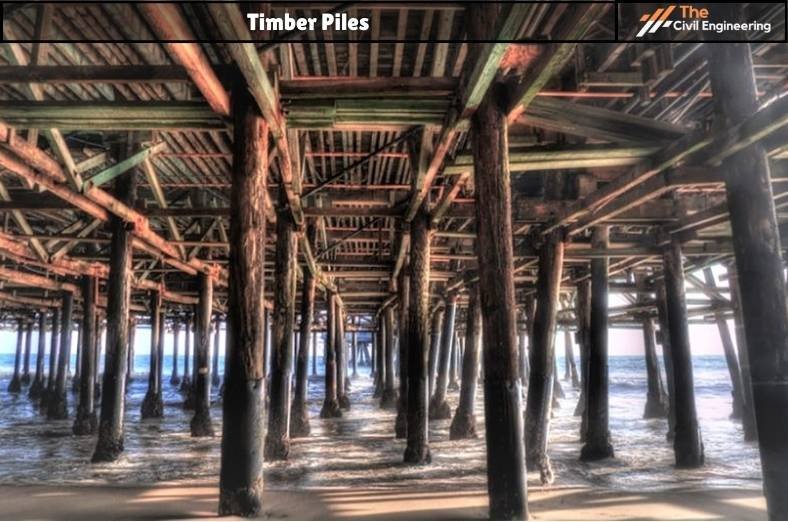

Figure: Timber Piles
Advantages of Timber Piles
Some of the advantages of these piles can be listed as follows:
1. Timber piles are economical because of the easy availability of timber.
2. The installation process is relatively simple and easy.
3. The timber piles can be cut to the desired length even after installation and it has a lower possibility of damage.
4. In case, timber piles have to be removed, they can be easily pulled out.
Disadvantages of Timber Piles
Some of the disadvantages of these piles can be listed as follows:
1. Timber piles cannot be used as end-bearing piles.
2. The driving of timber piles is extremely difficult in the hard soil layer.
3. If proper care is not taken, defects may occur in timber.
4. Treatment of timber such as the application of preservatives must be carried out.
Quality of Timber Piles
Timber piles should have the following properties:
a. It should be free from defects and have sound quality.
b. It should be straight.
c. It should have a uniform taper.
d. It should be free from defects (decay, splits, the twist of wood grains, etc.), knots & holes, etc.
Classification of Timber Piles
Timber piles can be classified into the following types based on ASCE Manual no 17 in the section entitled “Timber piles and Construction Timber”:
| Class A pile | The minimum diameter for this class of piles is 14 inches.
Use: These piles are to be used for heavy loads or large unsupported lengths. |
| Class B pile | The minimum diameter for this class of pile ranges between 12 to 13 inches.
Use: These piles are used for medium loads. |
| Class C pile | The minimum diameter for this class of piles is 12 inches.
Use: These piles are used for a temporary structure. |
Preservative Treatment of Timber Piles
✔ As timber piles have to resist moisture, insects, fungi, termites, and different chemical and weathering effects.
So, timber piles should be well treated with preservatives to improve resistivity and durability.
✔ Commonly sufficient amount of creosote oil is impregnated properly in the timber piles for the preservation and to improve immunity against moisture, chemicals, insects, etc.
Cutting, drilling, and framing work should be done before the application of creosote oil.
Abrasions and cuts should be covered with coats of creosote to prevent decay and biological as well as chemical attacks.
Over Driving of Timber Piles
✔ Damage due to overdriving is one of the major drawbacks of the timber piles. Damage may occur at the tip or above. So, the design capacity of timber piles should be limited to 25 tons to prevent damages due to overdriving.
✔ Blows per foot of penetration and behavior of pile upon load should be examined carefully. If there is any doubt of damage or possibility of damage; driving of piles should be stopped immediately and pulling out of two or more piles may be done to carry out the visual examination.
ii. Concrete Piles
Concrete piles essentially consist of concrete as the chief element.
Concrete piles may be further classified into precast concrete piles and cast-in-situ concrete piles.
They are briefly described as follows:
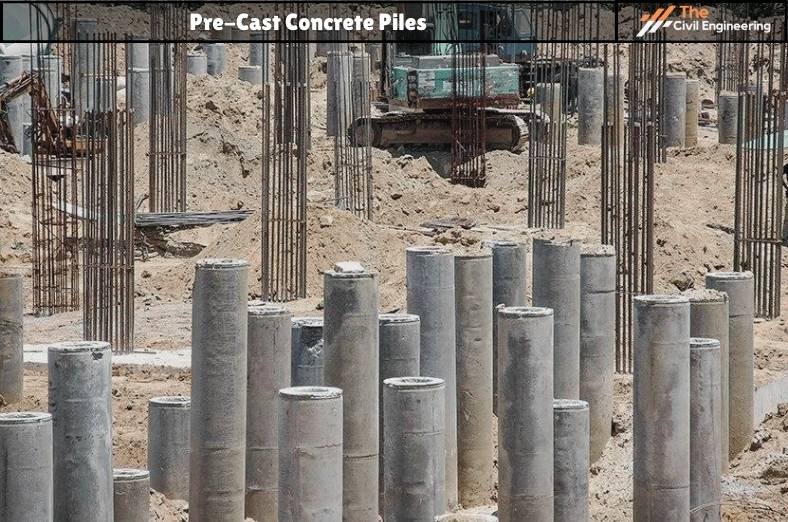
a. Pre-Cast Concrete Piles
Pre-cast concrete piles are manufactured in a casting yard and cured properly. Piles are then transported to the place where they are installed.
They can be driven to a length of 27 m and can have a capacity of up to 60 tons.
Usually, rectangular piles are cast in horizontal form whereas circular piles are cast in vertical form.
Pre-cast concrete piles may be reinforced or unreinforced.

Advantages of Pre-Cast Piles
Some of the advantages of pre-cast concrete piles can be listed as follows:
1. Pre-cast piles have high strength and stability.
2. They can withstand a load of high intensity.
3. Precast piles have high resistance to corrosion and biological defects and remain unaffected by groundwater.
4. Such piles can be used in almost all types of construction including marine constructions.
5. Precast concrete piles have high durability and are cost-effective.
Disadvantages of Pre-Cast Concrete Piles
Some of the disadvantages of pre-cast concrete piles can be listed as follows:
1. The change of length of such piles and mobilization is difficult.
2. Driving the piles requires heavy and advanced equipment.
3. There is a high risk of breakage of piles during the handling or driving operation.
b. Cast-in-Situ Concrete Piles
Cast in situ pile is formed by driving a closed-ended tubular section to form a void and then filling the void with concrete whilst withdrawing the section. Examples: Various systems such as Franki piles, Vibro piles, Alpha piles, and so on.
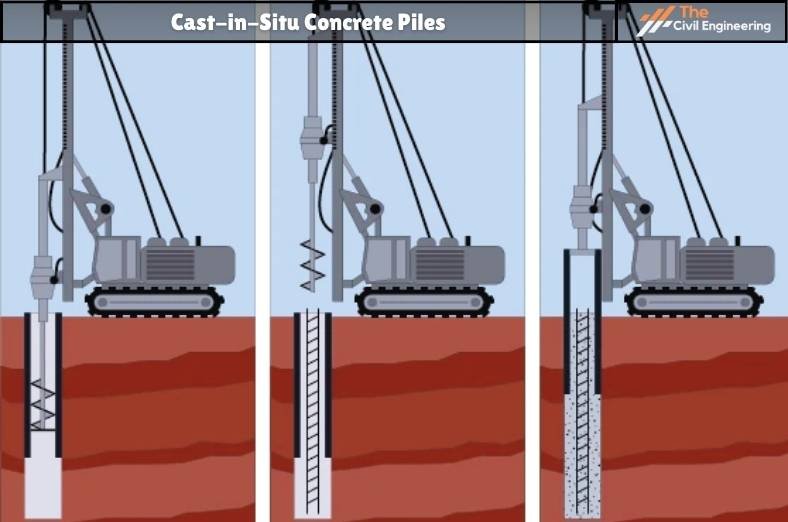
Advantages of Cast-In-Situ Concrete
Some of the advantages of cast-in-situ concrete piles can be listed as follows:
1. They are more flexible in terms of length variation.
2. Handling such piles is easier.
3. Additional piles may be provided easily.
4. The installation process is simple with no possibility of breakage.
Disadvantages of Cast-In-Situ Concrete
Some of the disadvantages of cast-in-situ concrete piles can be listed as follows:
1. Since the pile is cast in situ, a proper storage place must be arranged for storing the construction materials safely.
2. Quality control is quite difficult.
3. The difficulty may arise in casting the concrete where the underground flow of water is relatively heavy.
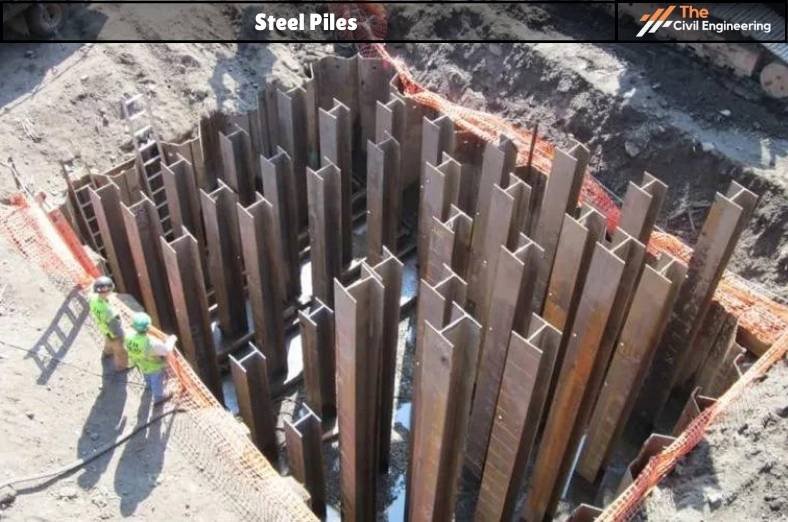
iii. Steel Piles
Steel piles are the type of pile foundation that is made up of steel sections. Commonly used steel piles include H-section piles, I-section piles, and screw piles.
Steel piles are used where hard driving is required. Pipe piles are driven open-ended or close-ended. They are often filled with concrete after driving.
The rolled steel sections can be driven upto36 m in length and can take a load up to 170 tons.
Screw piles can have lengths up to 24 m and working loads up to 250 tons are possible.
Steel piles are mostly used as end-bearing piles. They are usually designed in smaller sections with a diameter ranging between 10 inches to 24 inches.

Advantages of Steel Piles
Some of the advantages of steel piles are listed as follows:
1. Due to the smaller sectional area, such piles are easy to handle.
2. Steel piles can be driven easily through hard strata of soil and can be taken up to deeper depths.
3. Steel piles can withstand heavy loads.
Disadvantages of Steel Piles
Some of the disadvantages of steel piles can be listed as follows:
1. Steel piles are comparatively expensive.
2. Such piles are prone to corrosion.
iv. Composite Piles
Composite piles generally consist of two or more different materials usually one mounted over the other such that they function as a single unit.
For example, composite piles may be constructed of steel and timber or steel and concrete, etc.
Such piles have a very high capacity for taking loads.
| Read Also: Earth Moving Equipment With Images |
| Read Also: Soak Pit |

