Scaffolding is a temporary rigid structure to facilitate masons as a “platform to work as the building height increases.
Or,
The temporary network erected to support several platforms for the convenience of workers is called scaffolding.
When the height of the wall or column or other structural members of a building exceeds about 1.5 m, temporary structures are required to support the platform over which the workmen can sit and continue the construction. These temporary structures which are built very close to the surface of the wall generally in the form of timber or steel framework are said to be scaffolding.
For safety and integrity, each and every component of the scaffold should be checked properly before use.
1. Components or Parts of Scaffolding
Scaffolding consists of the following components that are as folows:
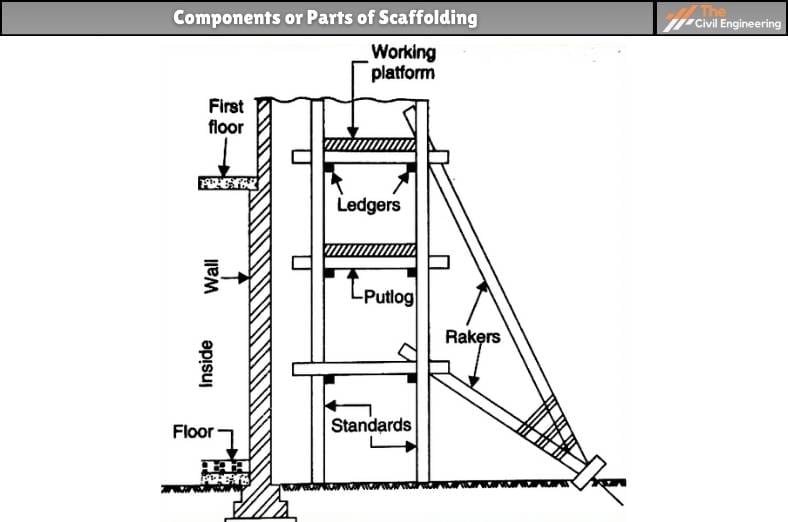
a. Standards:
Standards are the vertical member which is embedded into the ground for the support of scaffolding. These vertical members are spaced at 2.4 – 3.0 m.
b. Putlogs:
Horizontal member supporting platform and resting on ledgers is putlog. This is normally 90 cm in length and spaced at 1.2 m.
c. Braces:
Bracing members are tied diagonally to stiffen the scaffolding. Braces are poles tied by ropes.
d. Ledger:
It is a horizontal member which is parallel to the wall firmly fixed in the standard and provides support to the putlog. It is vertically spaced at 1.2–1.5 m.
e. Boarding:
These are the horizontal platform used by masons to support workmen and material. These are supported on the putlogs.
f. Railing:
This is a rail, provided like a ledger, at the working level.
g. Transoms:
If putlog is supported by ledgers on both ends then it is called transoms.
2. Uses of Scaffolding
1. It is used to provide a platform to work for masons.
2. It is used when painting work is carried out at heights.
3. It is used during the maintenance and cleaning of tall buildings.
4. It is used to support the materials during the construction at heights.
| Read Also: Shoring, Types of Shoring |
| Read More: Formwork |
3. Types of Scaffolding
There are 7 types of scaffolding that are commonly used. They are:
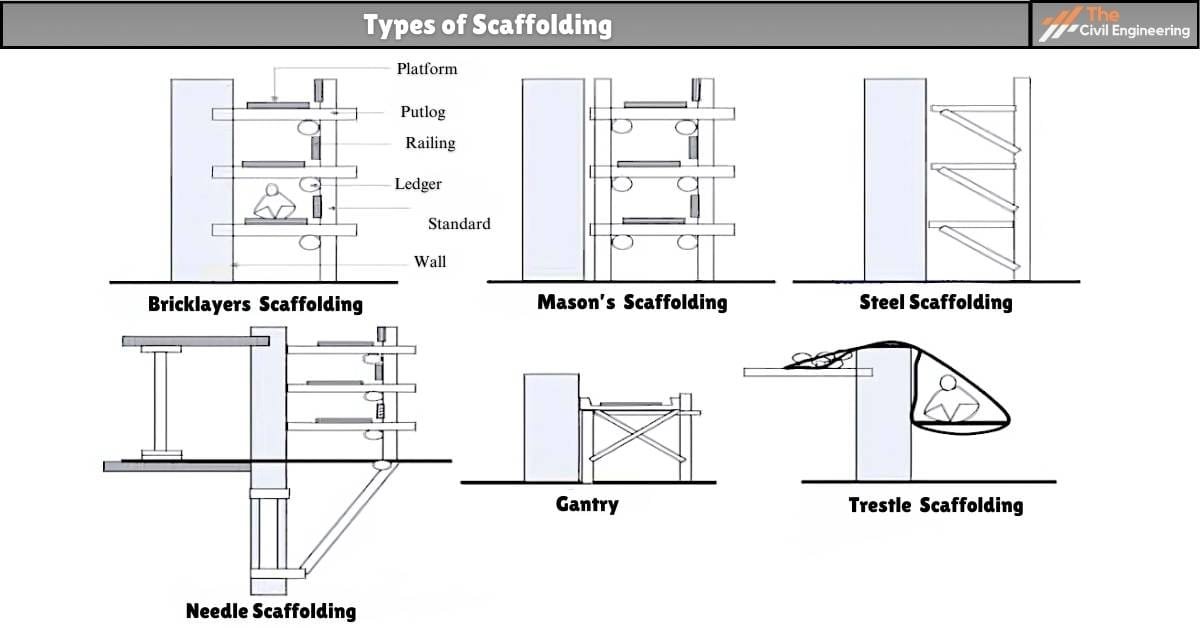
a. Single Scaffolding / Bricklayers Scaffolding
Single scaffolding is constructed parallel to the wall at a distance of about 1.2 m and generally consists of a single framework of standards, putlogs, ledgers, etc. It is also known as putlog scaffolding.
This type of scaffolding is erected by driving into the ground a single row of standards at 1.5 – 3.0 m c/c ( generally, 2.4 meters c/c).
Ledgers are connected to the standards and are provided at a vertical interval of 1.2 m to 1.5 m.
One end of the putlog is laid on the ledger and another end of the putlog is in the hole left in the wall, at an interval of 1.2 to 1.5 m.
The distance between the standards is about 2 m to 2.5 m.
Cross braces are also used for strength and stability.
This scaffolding is mostly used in wall construction (or bricklaying) and is less expensive.
b. Double or Masonry Scaffolding
Double scaffolding is used when it is not possible to make a hole into the wall to insert putlog and also where the cheap single type of scaffolding cannot be used, for example in stone masonry work. It is also known as independent scaffolding.
It is generally provided with two rows of standards for better performance and to provide a strong platform. A separate vertical framework is formed in each row.
The first row is placed 20 – 30 cm away from the wall while the other framework is placed at 1m distance from the first one.
The two rows are secured by ledgers which fulfill the same function as the ‘putlogs‘ in the single scaffold.
To prevent slippage of the scaffold; diagonal braces & raking shores can also be installed.
c. Cantilever or Needle Scaffolding
Cantilever scaffolding is used under the following circumstances:
a. Ground is weak to support the standards.
b. Construction of an upper part of the wall is to be carried out.
c. It is required to keep the ground, near the wall, free for traffic, etc.
d. Steel Scaffolding
Steel scaffolding is practically similar to timber scaffolding except that wooden members are replaced by steel tubes and steel couplets(fittings).
This scaffolding has greater strength, greater durability, and higher fire resistance.
It is reliable scaffolding used for both brick walls and stone walls.
As steel is expensive to purchase initially, but later it requires less maintenance and repair costs.
e. Suspended Scaffolding
Suspended scaffolding is used for outer works, decorative works, etc. that includes pointing, painting, repairs, etc.
This type of scaffolding uses wire ropes or chains connecting from the roof of the building up to the working platform.
The wire ropes or chains can be adjusted ( either raised or lowered) according to the requirement of the work.
Suspended scaffolding must be flexible, lightweight, and strong enough to carry a person safely and easily.
f. Patented Scaffolding
Patented scaffolding is the modified scaffolding made up of steel and a special arrangement of couplings, frames, etc. such that this type of scaffolding can be adjusted on the working platform with stable support braces up to a certain height.
g. Trestle Scaffolding
The scaffolding in which the working platform is supported on movable ladders or tripods is trestle scaffolding.
This scaffolding is mostly used for interior works like painting, repairing, decorating, etc.
It is applicable only up to 5 m in height for repairing and painting purposes.
4. Safety Measures of Scaffolding
To prevent and reduce the percentage of scaffold accidents, here are some of the safety measures:
a. Properly trained workers should be engaged in work by wearing adequate PPE.
b. Scaffold should have a handhold above its platform.
c. Adjustment of leg screws of the scaffold should not exceed 12 inches.
d. Safety belts and lanyards should be used at a height of 10 feet or more above the ground level.
e. Plank is overlapped or not should be checked to avoid movement.
f. There should be the use of a net below the working platform of the scaffold to catch falling objects or persons.
g. Wheels of scaffolds should be stabilized with a stone lock preventing rolling or moving of scaffolding.
5. Precautions to be taken for scaffolding safety
The precaution that needs to be carried out while working on scaffolding is as follows:
a. Scaffolds should not be stood in slippery or muddy or snowy places.
b. Don’t overload the scaffolds beyond their weight-carrying limit.
c. Feet should be kept on the decking properly.
d. Don’t lean on the scaffolds to avoid hazardous movements.
e. Scaffolds component’s stability should be checked properly.
f. Only Inspected tagged scaffolds should be used.
GREEN denotes Safe For Use.
YELLOW denotes Caution! (Warning!)
RED denotes Danger (Unsafe For Use)
Read More: Plinth Beam
Read Also: Formwork, Types of Formwork

